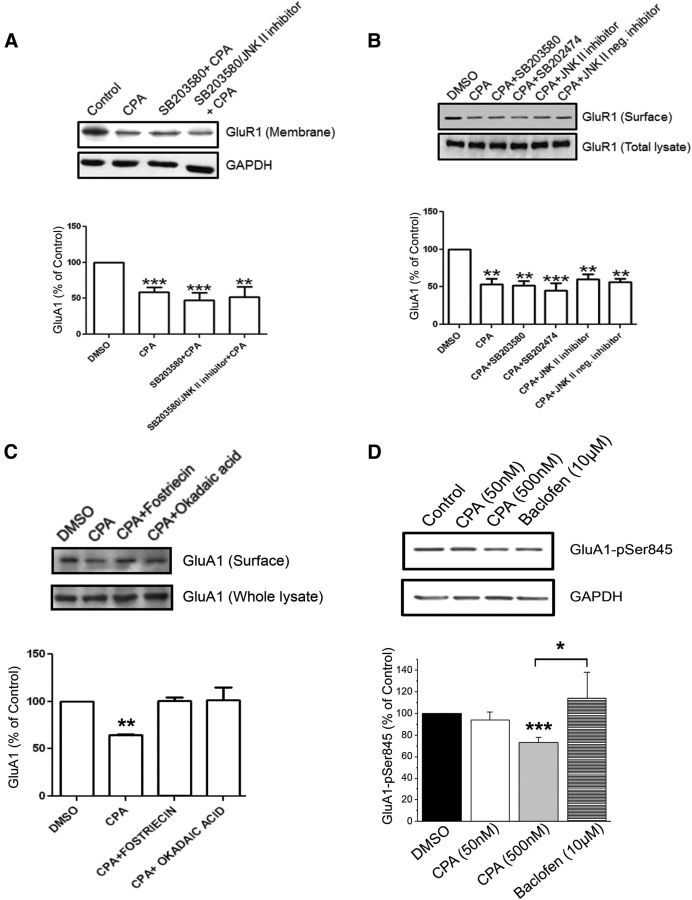
Figure 7.
A1R-mediated internalization of GluA1-containing AMPARs in hippocampal slices is not regulated by p38 MAPK or JNK but is regulated by PP2A, and robust A1R activation reduced GluA1-Ser845 phosphorylation. A, Levels of GluA1 (top) and GAPDH (bottom) in the membrane fraction of hippocampal slice lysates with preincubation in DMSO (control), SB203580 (20 μm), or SB203580 and JNK II inhibitor (5 μm) together followed by CPA treatment (500 nm, 45 min). Preincubation in either SB203580 or SB203580 and JNK II inhibitor together did not prevent A1R-induced GluA1 internalization. B, Surface biotinylation of hippocampal slices showing that A1R-mediated GluA1 internalization did not depend on the activity of p38 MAPK and JNK. Compared with GluA2, drug treatments with SB203580 (20 μm), but not the inactive analog SB202474 (20 μm), or JNK II inhibitor (5 μm), or the inactive analogs of SB203580 (SB202474, 20 μm), or JNK II inhibitor (JNK II neg. inhibitor, 5 μm), did not prevent A1R-induced internalization of GluA1. C, Preincubation of hippocampal slices in the PP2A inhibitors okadaic acid (20 nm) or fostriecin (20 nm) for 1 h followed by CPA treatment (500 nm, 45 min) prevented A1R-induced internalization of GluA1. D, Whole lysates of hippocampal slices treated with CPA (50 or 500 nm, 45 min) or the GABAB receptor agonist baclofen (10 μm, 45 min) and probed for the C-terminal phosphorylation site GluA1-pSer845. The antibody used was specific for phosphorylated Ser845 (pSer845) of GluA1. CPA treatment of 500 nm caused a robust decrease in pSer845, whereas baclofen and 50 nm CPA did not. All values in summary bar charts are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001.