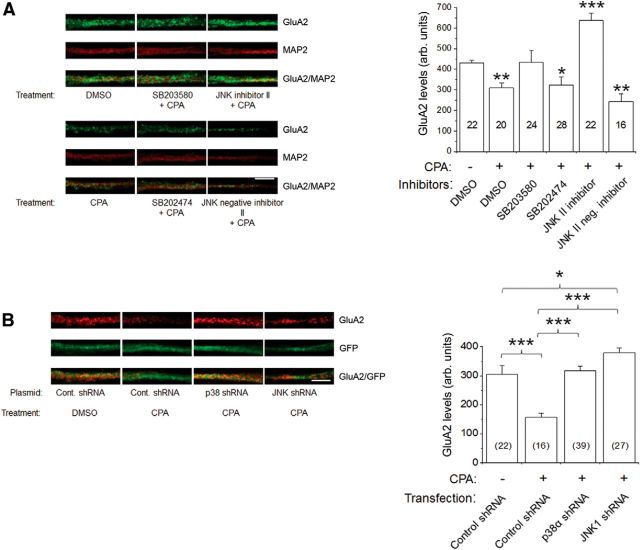
Figure 8.
A1R-mediated decrease in GluA2 surface levels in primary hippocampal neurons was prevented by pharmacological inhibitors and genetic knockdown of p38 MAPK and JNK. A, Intensity levels of surface-expressed GluA2 were determined by confocal imaging and analyzing 10 μm dendritic lengths located 5 μm away from cell somas. Results showed that A1R-induced GluA2 endocytosis was inhibited by p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 (20 μm), but not by inactive analog SB202474, and JNK II inhibitor (5 μm), but not by its inactive analog JNK II-negative control. The compounds SB203580, SB202474, JNK II inhibitor, and JNK II-negative inhibitor were applied to hippocampal neurons for 1 h before CPA treatment (500 nm, 45 min). Surface GluA2 (green) was detected by using an antibody directed against the extracellular epitope of GluA2 in nonpermeabilized conditions, then subsequently permeabilized and stained with chicken anti-MAP2 antibody (red). The p38 MAPK and JNK inhibitors did not significantly affect CPA-mediated GluA1 internalization (see Results). B, Using an shRNA knockdown strategy, the shRNAs p38α MAPK and JNK1 prevented A1R-induced GluA2 internalization. Cultured neurons transfected with the control plasmid A (GFP-fluorescent), p38α MAPK, or JNK1 shRNA were treated with DMSO or CPA (500 nm, 45 min) and subsequently labeled with GluA2 and MAP2 as in A. CPA-induced GluA2 internalization was prevented by transfections of p38α MAPK and JNK1 shRNA plasmids. Average GluA2 intensity values in summary bar charts represent the mean ± SEM from 3 transfections, with the number of neurons indicated inside brackets. *p < 0.05 versus control. **p < 0.01 versus control. ***p < 0.001 versus control. Statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA, followed by post hoc Student-Newman-Keuls test. Scale bars: A, B, 2 μm.