Figure 1.
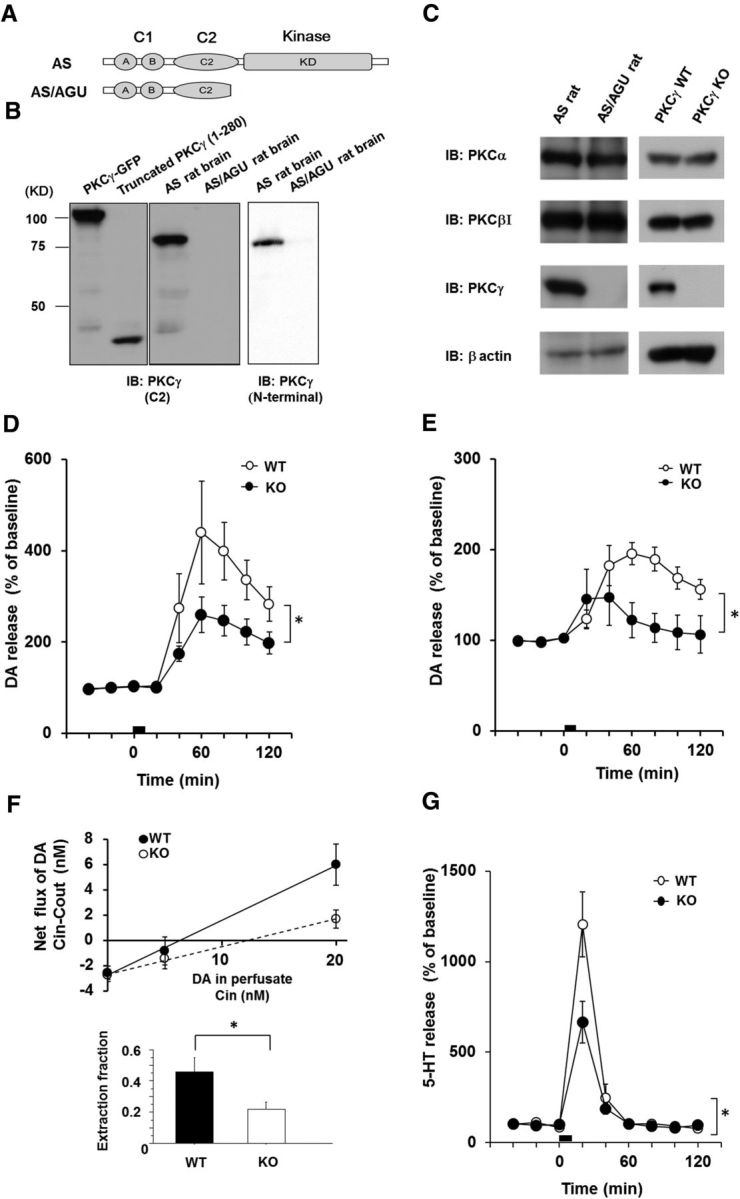
The PKCγ KO model exhibits symptoms of parkinsonian syndrome. A, Schematic illustrations of the PKCγ protein and AS/AGU mutations. The truncated PKCγ polypeptide terminates within the C2 domain. B, Recombinant truncated PKCγ (1–280 aa), which was transfected in COS-7 cells, the AS rat brain lysate, and the AS/AGU rat brain lysate, was detected by immunoblot analysis with an anti-PKCγ (C2-domain) monoclonal antibody and anti-PKCγ (N terminal) antibody, respectively. C, The PKCγ KO was confirmed by immunoblot analysis of the whole brain of the AS/AGU rats and PKCγ KO mice. Arrowheads are recombinant PKCγ-GFP and PKCγ (1–280aa)-GFP, which were used as positive controls. D, In vivo microdialysis in the striatum of the PKCγ KO mice. A high level of K+ was perfused into the striatum through a dialysis probe for the time indicated by the square at 3–4 months. The results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4–5, interaction of the genotype and time for DA release that was stimulated by high K+ levels; *p < 0.05, F(8,48) = 2.31, repeated two-way ANOVA). E, In vivo microdialysis for DA in the striatum of the PKCγ-KO (KO) mice that were stimulated with METH. METH (1 mg/kg) was perfused into the striatum through a dialysis probe for the time indicated by the square at 3 months (n = 4, interaction of the genotype and time for DA release stimulated by METH, F(8,48) = 3.37; *p < 0.01, repeated two-way ANOVA). F, No-net flux microdialysis to quantitate basal DAT activity in PKCγ KO mice. Three different concentrations of DA in CSF (0, 5, and 20 nm DA) were perfused through the probes to determine the extracellular DA concentration and extraction fraction. Linear regression for the DA perfused and DA measured provided extraction fraction (slope) as an indirect measure of DAT activity in vivo to remove extracellular DA. Extraction fraction for WT and KO mice are shown. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 4 and 5 for WT and KO mice, respectively, *p < 0.05). G, In vivo microdialysis of serotonin in the striatum of the PKCγ-KO mice that were stimulated by high K+ levels. K+ (100 mm) was perfused into the striatum through a dialysis probe for the time indicated by the square at 3–4 months. The results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4, interaction of the genotype and time for serotonin release that was stimulated by high K+ levels, F(8,48) = 5.399; *p < 0.001, repeated two-way ANOVA).
