Figure 2.
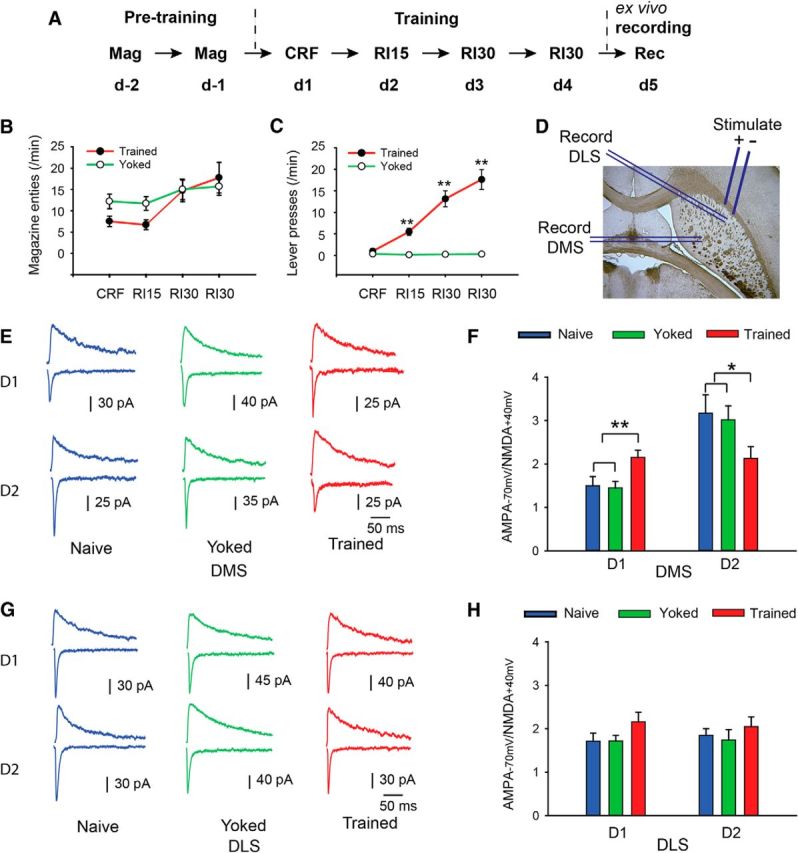
Ex vivo electrophysiological assessment of plasticity in D1R- and D2R-expressing SPNs in the pDMS after action–outcome learning. A–C, D2-GFP mice were given training sessions in which reward delivery was either paired with lever pressing (trained) or unpaired with lever pressing (yoked). Rate of magazine entries (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA, F(1,117) = 0.5, p > 0.05; n = 22 and 19 for trained and yoked mice, respectively) and rate of lever presses (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA, F(1,117) = 50.5, p < 0.01; post hoc test, **p < 0.01) were recorded and compared between the yoked and the trained mice. D, Parahorizontal striatal slices were prepared, and the stimulation electrode was placed at the white matter between the cortex and the dorsal striatum, and either GFP-positive or GFP-negative neurons in the pDMS or the DLS were recorded. E–H, In the trained and yoked groups, the induction of action–outcome learning had a clear effect on plasticity with the D1R-expressing SPNs in the pDMS demonstrating a higher AMPA/NMDA ratio in the trained group than in the yoked or naive groups. Conversely, the D2R-expressing SPNs in the pDMS demonstrated a lower AMPA/NMDA ratio in the trained group than in the yoked or naive groups (E, F), indicating opposing changes in plasticity in the D1- and D2-expressing neurons. For D1 neurons in the pDMS, one-way ANOVA revealed no difference between naive versus yoked groups (F < 1), but a significant difference between the trained group and both the naive and yoked groups (F(1,46) = 10.9, p < 0.01; post hoc test, **p < 0.01). n = 13–22. For the D2 neurons in the pDMS, the naive and yoked groups again did not differ (F < 1). However, the trained group differed from both the naive and yoked groups (F(1,41) = 5.70). *p < 0.05. n = 13–15. Furthermore, these effects were only found in the pDMS and did not extend to the DLS: the AMPA/NMDA ratio of the D1R- and D2R-expressing SPNs in the DLS was not significantly different between the trained and yoked or naive groups (G, H: ANOVA, p > 0.05, n = 12–19).
