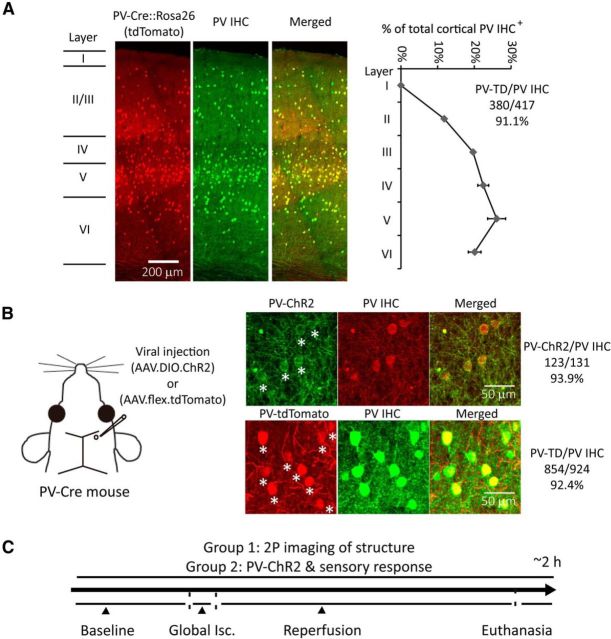
Figure 1.
PV-Cre-dependent expression within PV interneurons and experimental design with global ischemia and reperfusion model. A, Confocal fluorescence images of coronal sections through layer I to VI in the forepaw somatosensory cortex of PV-Cre line crossed with the ROSA-tdTomato reporter line (PV-Cre × Ai9) show overlay between PV-Cre expression and PV-antibody immunohistochemical (IHC) staining. Layer borders are indicated on the left. Ratios of PV IHC+ cells distributed through layer I to VI and tdTomato expressed cells/PV IHC+ cells are shown on the right (mean ± SEM, n = 2). B, AAV1.DIO.ChR2-eYFP or AAV1.flex.tdTomato was injected into the somatosensory cortex (350–400 μm depth) of PV-Cre mice at ∼1 nl/s using glass pipettes (tips are <25 μm in diameter) at least 3 weeks before experiments. ChR2-eYFP or tdTomato expressing cells and PV IHC are shown. Stars indicate ChR2-eYFP (and tdTomato) and PV IHC+ colocalized cells. Ratio of viral-expressing cells to PV IHC+ cells is shown on the right. C, Experimental design: one group of mice with AAV1.flex.tdTomato injection was used to perform 2P imaging of PV-neuron structure; the other group of mice with AAV1.DIO.ChR2-eYFP injection is used to perform functional study of PV-neurons with optogenetic stimulation. Both groups of mice receive a 5 min CCAO-induced global ischemia followed by reperfusion. Isc, ischemia.