Figure 1.
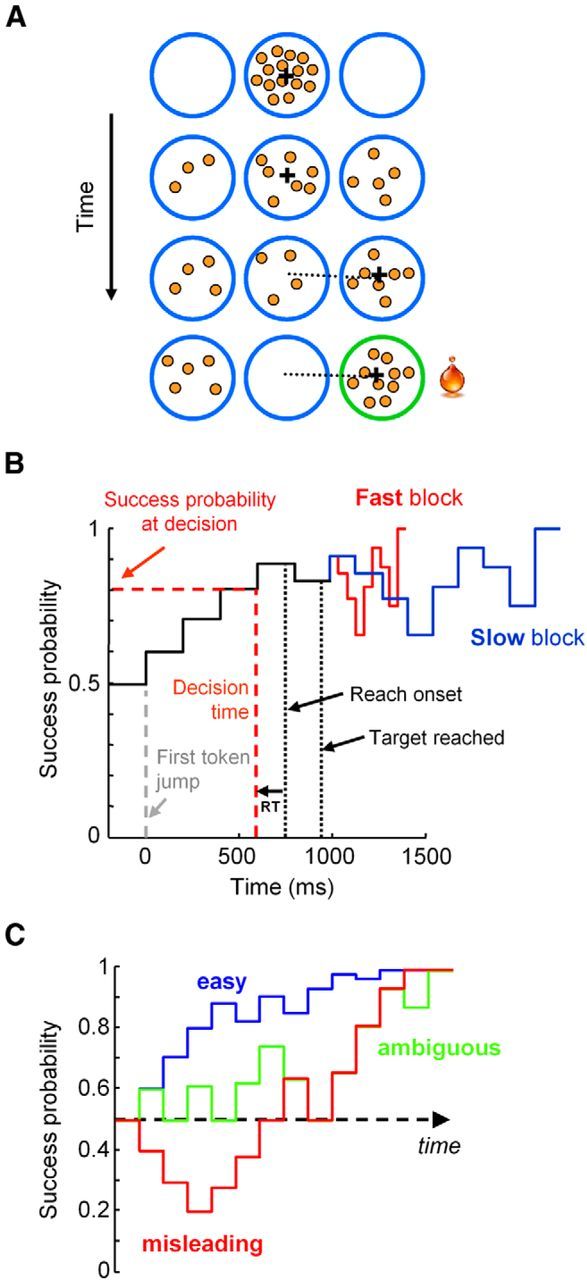
A, Schematic of the tokens task. B, Temporal profile of success probability in an example trial. The estimated time of the decision is computed by subtracting the monkey's mean reaction time (RT) in the delayed reach task from movement onset time, allowing computation of the success probability at that moment. C, Example success probability profiles of easy, ambiguous, and misleading trials. A trial is classified as “easy” if success probability (SP) exceeds 0.6 after two token jumps and 0.75 after five. A trial is ambiguous if the SP is 0.5 after two jumps, between 0.4 and 0.65 after three, and then between 0.55 and 0.66 after five and seven jumps. A trial is misleading if SP is <0.4 after three token jumps.
