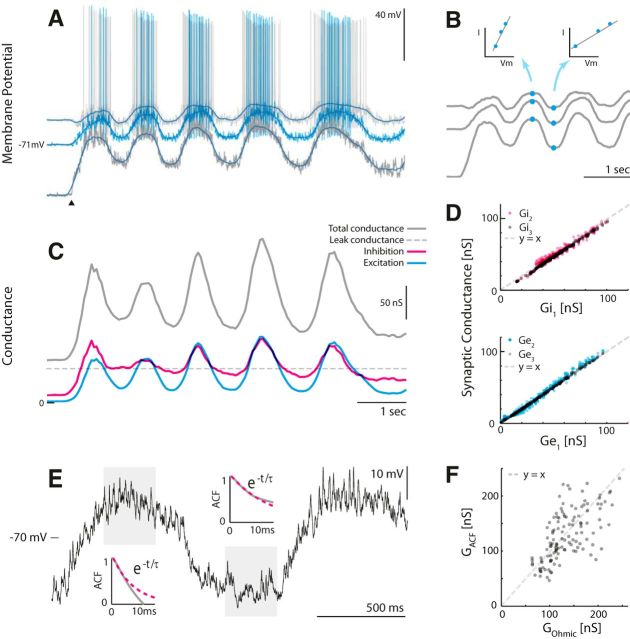
Figure 2.
The ohmic and the ACF methods for estimating synaptic inputs illustrated on transected sample data. A, The ohmic method requires at least two trials connecting Vm and current injection (Iinj) to estimate Gtot. Shown here are three trials each with constant but different Iinj. The onset of tactile induced motor behavior is indicated (▴). B, A low-pass filtering of the traces gives an I/V relationship as a function of time (indicated for two time points) where the slope is Gtot. C, The resulting time-dependent Gtot (gray), Ginh (magenta), and Gexc (cyan) using Eqs. 3 and 4. D, Linearity should be confirmed, for instance, by plotting the estimates for different depolarizations against each other. E, The ACF method. The total conductance is estimated via the membrane time constant (GACF = C/τm), which is estimated via autocorrelation decay. F, The estimates of the total conductance using the two methods have a significant correlation (r = 0.64, p ≪ 0.001). [Adapted from Berg and Ditlevsen (2013) with permission.]