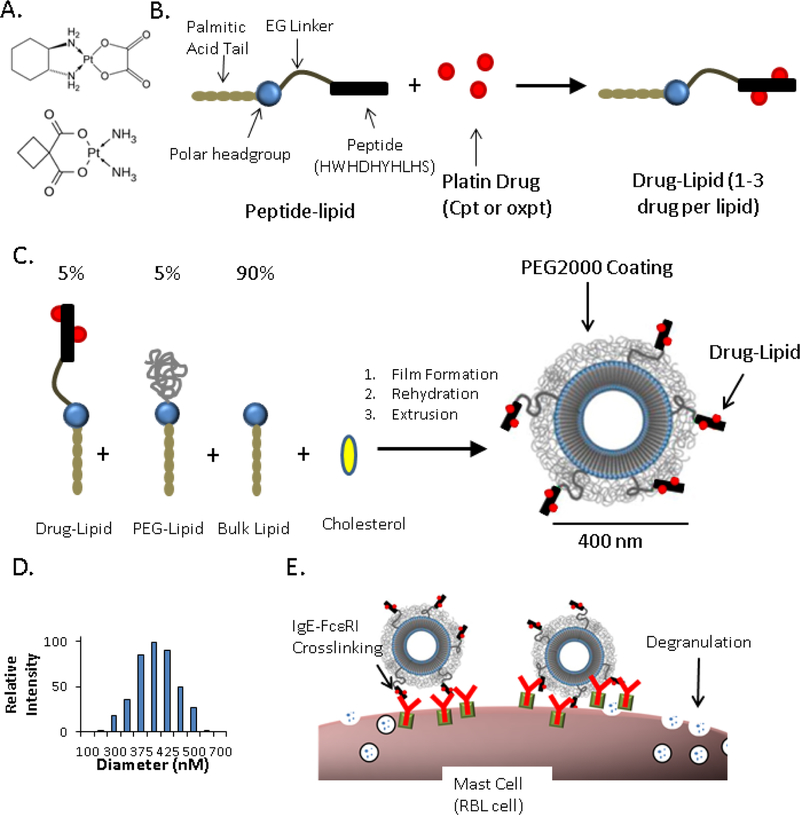
Figure 1.
Nanoallergen Design and Characterization. (A) Chemical structure of the two platin drugs used in this study, oxaliplatin (top) and carboplatin (bottom). (B) Drug-lipid synthesis. A peptide (HWHDHYHLHS) was conjugated to a lipid tail via an ethylene glycol spacer and then reacted with free platin drug (oxaliplatin or carboplatin) to form drug-lipids. (C) Nanoallergen synthesis. Drug-lipids, PEG- lipid and a bulk lipid (DSPC) were mixed at 5:5:90 ratio and cholesterol was added for improved stability (50% of total lipid), rehydrated and extruded through filters with 400 nm pore sizes. (D) Dynamic light scattering analysis of oxpt loaded liposomes confirmed a diameter of ≈400 nm. (E) Cartoon demonstration describing how nanoallergens crosslink drug specific IgE-FcεRI complexes on mast cell surfaces and trigger degranulation.