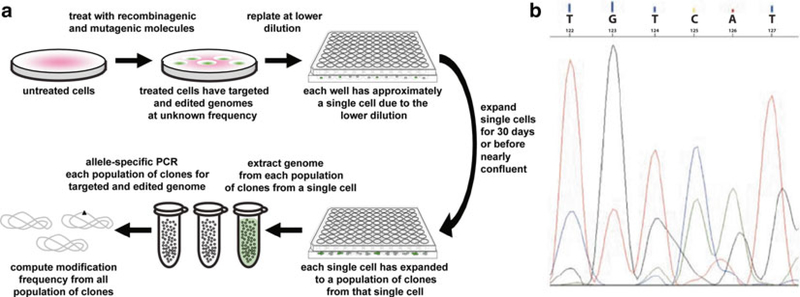
Fig. 6.
Quantifying recombinagenic and mutagenic frequencies of gene disruption with single-cell cloning assays of the CCR5 genomic locus. Single-cell cloning assays are used to (a) quantify the recombinagenic and mutagenic frequency of recombinagenic donor DNA alone or recombinagenic donor DNA co-transfected with mutagenic triplex-forming molecules, in the gene disruption of the CCR5 genomic locus by expanding each single cell to a population of clones sufficient in number to enable allele-specific PCR-based verification and calculation of modification frequency, (b) with sequencing chromatographic mixed peaks indicating a heterozygous clone (wild type sequence being TGTCAT; modified sequence being CTGAGG)