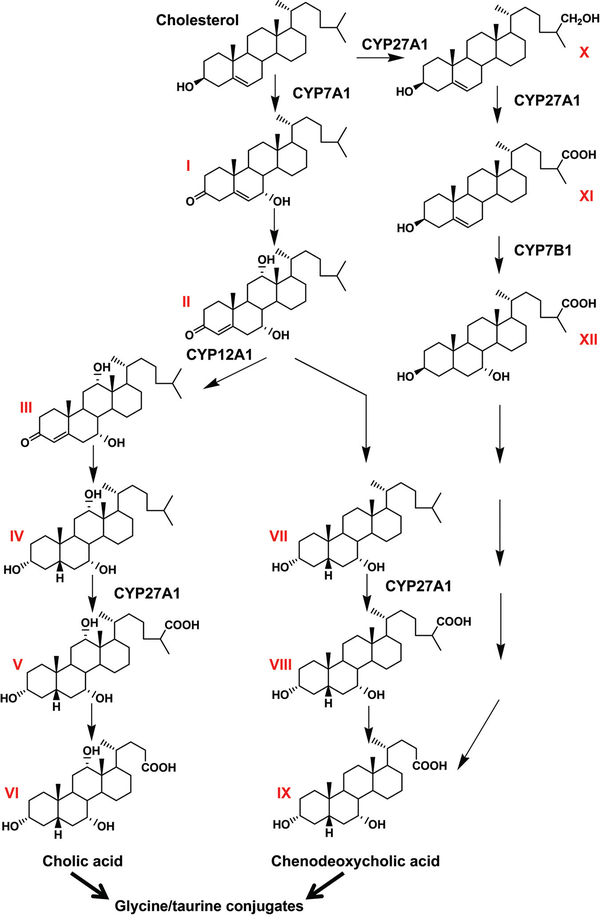
Figure 2.
Pathway for the synthesis of bile acids. Neutral pathway: cholesterol is converted to 7α-hydroxycholesterol (I) by CYP7A1, the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol degradation in the major neutral pathway of bile acid synthesis. 7α-Hydroxycholesterol is reduced to 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one (II), which is metabolized to 7α,12,-dihydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one (III) by CYP12A1 or reduced to 5β-cholestane-3α,7α-diol (VII). 7α,12,-Dihydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one is oxidized to 5β-cholestane-3α,7α,12,-triol (IV), and 5β-cholestane-3α,7α-diol is oxidized by CYP27A1 to 3α,7α-dihydroxy-5β-cholestanoic acid (VIII), which is then metabolized to the terminal metabolite chenodeoxycholic acid (IX) through a demethylation reaction. 5β-Cholestane-3α,7α,12,-triol is also oxidized to 3α,7α,12,-trihydroxy-5β-cholestanoic acid (V) by CYP27A1, which is converted to the terminal metabolite cholic acid (VI) by a demethylation reaction. Acidic pathway: cholesterol is also converted to 27-hydroxycholesterol (X) and 3β-hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid (XI) by CYP27A1 in the minor acidic pathway. 3β-Hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid is metabolized to 3β,7α-hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid (XII) by CYP7B1. A series of reactions converts 3β,7α-hydroxy-5-cholestenoic acid to chenodeoxycholic acid (IX). The author thanks Fei Li for making this figure.