Figure 5.
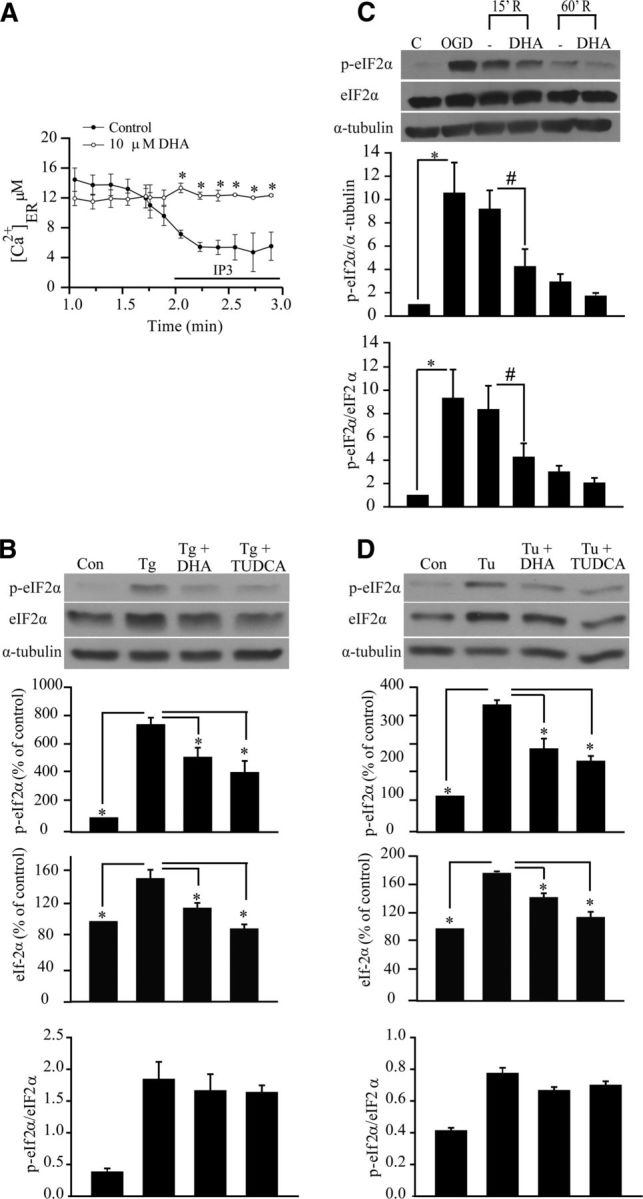
DHA prevents ER Ca2+ depletion and ER stress in neurons and astrocytes. A, Representative tracings of Ca2+ER release in response to IP3 in cultured cortical neurons. IP3 (10 μm) was applied to saponin-permeablized neurons to trigger the Ca2+ER release. DHA (10 μm) was added 2–3 min before permeabilization and present in the subsequent solutions. B, Representative immunoblot of p-eIF2α and eIF2α in primary cortical astrocytes. Cells were exposed to Tg (1 μm), DHA (10 μm), or TUDCA (10 μm) for 24 h. Expression of p-eIF2α protein, eIF2α protein, and the ratio of p-eIF2α versus eIF2α were analyzed. The same blot was probed with anti α-tubulin antibody as a loading control. Data are mean ± SE (n = 3). *p < 0.05 versus ER stressor. C, DHA attenuated expression of p-eIF2α protein in cortical neurons induced by OGD (2 h) and REOX (15–60 min). DHA (10 μm) was only present during 15–60 min REOX. Expression of p-eIF2α protein, eIF2α protein, and the ratio of p-eIF2α versus eIF2α protein were analyzed. The same blot was probed with anti α-tubulin antibody as a loading control. Data are mean ± SE (n = 4). *p < 0.05 versus control; #p < 0.05 versus REOX. D, Representative immunoblots of p-eIF2α and eIF2α in cortical astrocytes. Astrocytes were exposed to Tu (10 μg/ml), DHA (10 μm), or TUDCA (10 μm) for 24 h. Expression of p-eIF2α protein, eIF2α protein, and the ratio of p-eIF2α versus eIF2α protein were analyzed. The same blot was probed with anti α-tubulin antibody as a loading control. Data are mean ± SE (n = 3). *p < 0.05 versus ER stressor.
