Figure 3.
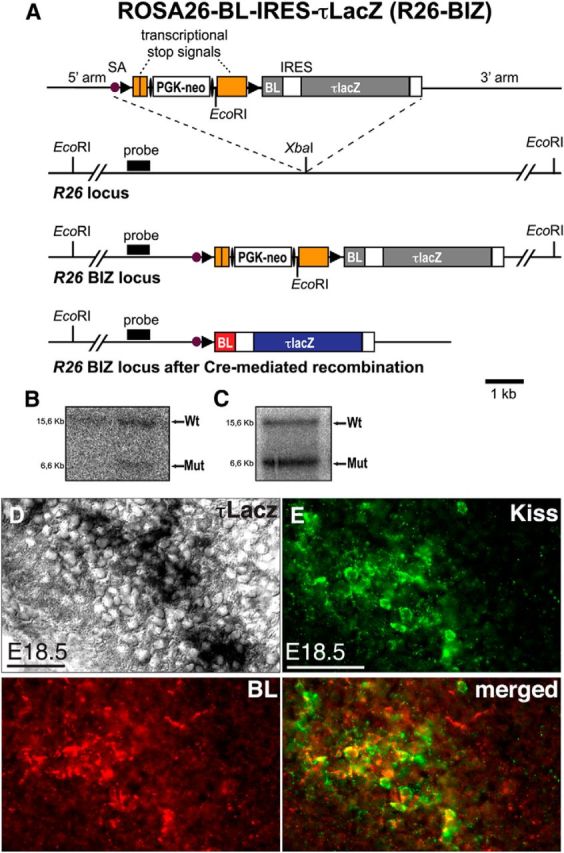
Targeted integration of a Cre-dependent BL-IRES-τlacZ transneuronal tracer into the R26 locus. A, Schematic representation of the targeting strategy. From top to bottom: the targeting vector, the wild-type R26 allele, and the targeted R26 allele before and after Cre-mediated recombination are shown. The targeting vector contains a loxP-flanked transcriptional stop cassette with an FRT-flanked phosphoglycerate kinase promoter-driven neomycin resistance gene (PGK-neo), and the coding sequence for BL-IRES-τlacZ. LoxP and FRT sites are indicated by solid arrowheads and ellipses, respectively. SA, Adenovirus splice acceptor sequence. B, Southern blot analysis of genomic ES cell DNA. The expected fragment sizes detected by the probe are indicated (wild-type, 15.6 kb; mutant, 6.6 kb). C, Germline transmission of the R26-BIZ allele was confirmed by Southern blot analysis of tail DNA. D, Histochemical analysis of β-galactosidase activity in a female KissIC/R26-BIZ brain at E18.5. The section is adjacent to the one shown in E. E, Antibodies against kisspeptin demonstrate faithful activation of BL in kisspeptin neurons. Scale bars: D, 20 μm; E, 50 μm. Wt, Wild type; Mut, mutant.
