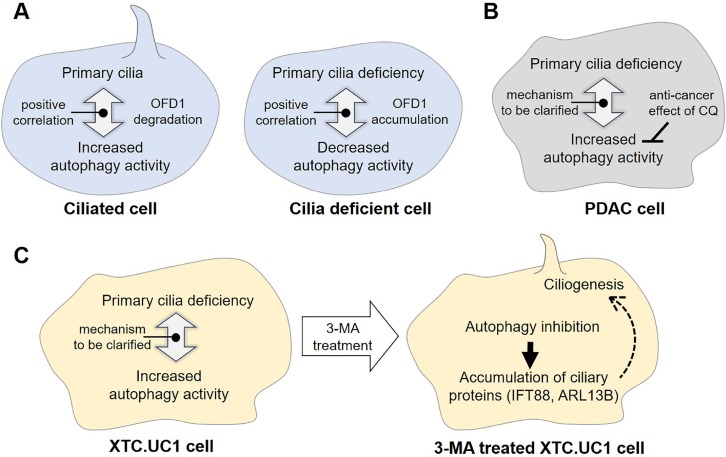
Fig. 1.
Controversial interplay between primary cilia and autophagy and effect of autophagy inhibitors in cancer cells. (A) Proposed model for the positive correlation between primary cilia and autophagy involving OFD1 protein in normal cells (B) Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells with increased autophagy activity despite absence of primary cilia. In this cancer cell, the autophagy inhibitor, chloroquine (CQ), shows therapeutic effect. (C) XTC.UC1 cells derived from thyroid Hürthle cell carcinoma with increased autophagy activity despite decreased frequency of ciliated cells. In this cancer cell, the autophagy inhibitor, 3-MA, increases frequency of ciliated XTC.UC1 cells via accumulation of ciliary proteins, such as IFT88 and ARL13B.