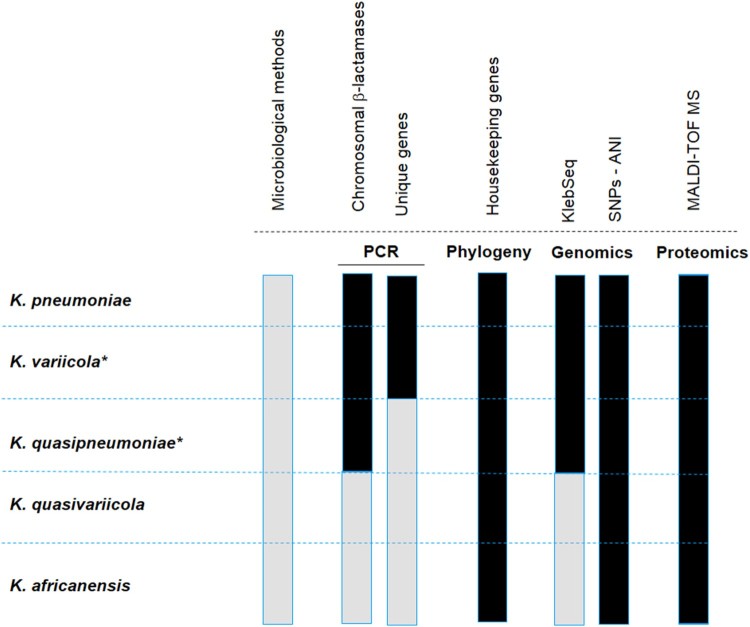
Figure 1.
Representation of the available methods that allow differentiating the K. pneumoniae complex. The black colour means that the indicated method distinguishes the species of the K. pneumoniae complex, and the grey colour implies the opposite. Microbiological methods refer to standard biochemical procedures. PCR refers to molecular methods based on the amplification of chromosomal β-lactamases or unique genes assembled in a multiplex PCR, or single PCR such as yggE. The phylogenetic analysis corresponds to the most commonly used gene, rpoB. KlebSeq is a sequencing tool for screening and epidemiological surveillance of the Klebsiella genus. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have been used for the differentiation of some species of the K. pneumoniae complex, but they are definitely feasible for all species of the complex. The average nucleotide identity (ANI) is a genomic tool used for species differentiation and is highly recommended for this purpose. With the recent update of the proteomic profile of the K. pneumoniae complex, it is possible to differentiate the species that constitute the K. pneumoniae complex by using MALDI-TOF. The Bruker reference library version 6.0.0.0 includes the reference spectra for proper identification of K. variicola from K. pneumoniae but not for the rest of the members of the K. pneumoniae complex. The asterisk symbol behind the species name means that the subspecies are included, for instance K. variicola subsp. variicola, K. variicola subsp. tropicalensis, K. quasipneumoniae subsp. quasipneumoniae and K. quasipneumoniae subsp. similipneumoniae.