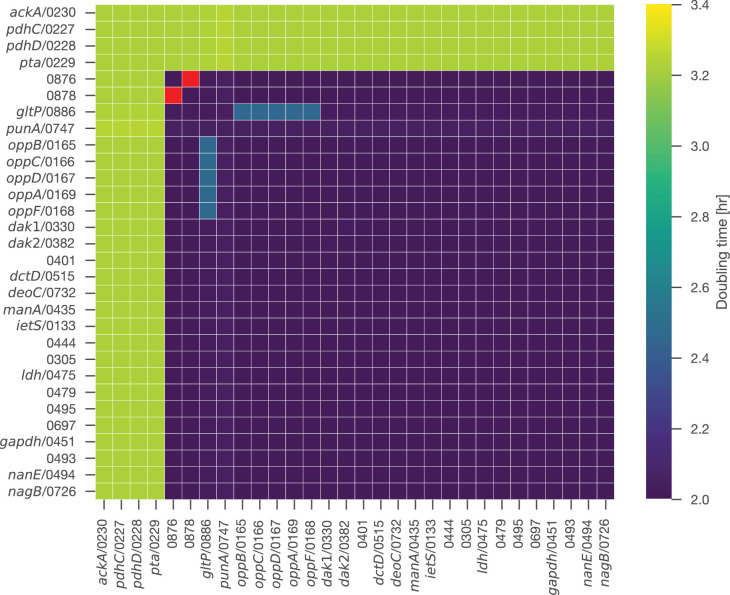
Among the individually non-essential genes, a double knockout of the gene pair (0876, 0878) is the only lethal combination (red). This knockout corresponds to simultaneously removing both amino acid permeases, thus preventing cysteine uptake. Simultaneous knockout of the glutamate/aspartate permease gltP/0886 and any Opp gene (oppB/0165 through oppA/0169) is non-lethal in silico, as the model will under these circumstances produce glutamate through the hypothesized dUMP breakdown reaction CTPSDUMP and, to a lesser extent, through the reaction CTPS2 (both catalyzed by pyrG/0129). Glutamate production through pyrG/0129 is not expected to be able to meet cellular demands in vivo. If flux through CTPSDUMP is set to zero in the model, a double knockout of gltP/0886 and Opp becomes lethal in silico.