Fig. 2.
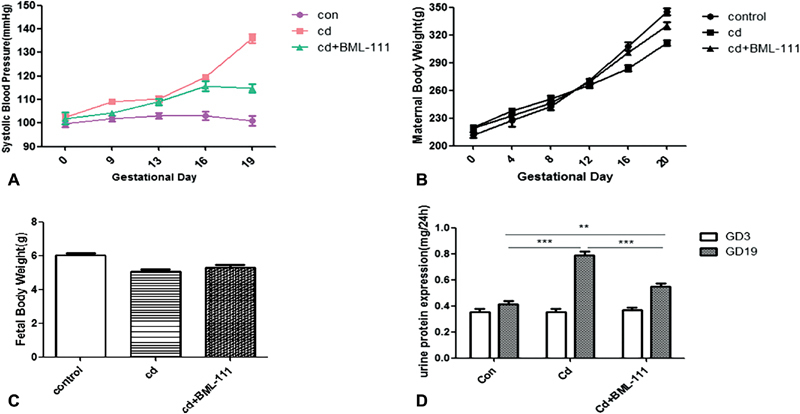
BML-111 treatment improves the symptoms of preeclampsia (PE) model rats. Pregnant rats were intraperitoneally injected with sterile saline (control group) or 0.125 mg/kg cadmium chloride (CdCl 2 ) (Cd group) on day 9 to 14 of pregnancy. BML-111 (Cd + BML-111 group, 1 mg/kg/day) was administrated intraperitoneally injected after Cd administration from day 14 of pregnancy and at the rate of once per day for 6 days. ( A ) The systolic blood pressures (SBPs) of the Cd group at days 13, 16, and 19 of pregnancy were 110.3 ± 2.06, 119.5 ± 2.1, and 136 ± 3.39 mm Hg, respectively ( n = 8, p < 0.05, vs. the control group at the corresponding time point). BML-111 treatment significantly alleviated SBP to 114.8 ± 2.95 mm Hg on days 19 of pregnancy, respectively ( n = 8, p < 0.05, vs. the Cd group). ( B ) The maternal body weight gain of the Cd group (94.33 ± 4.14 g) was significantly lower compared with that of the BML-111 administration group (111.33 ± 3.09 g, n = 8, p < 0.05). ( C ) The fetal weight of the Cd group was not apparently different compared with that of the placebo and BML-111 administration groups ( p > 0.05). ( D ) Twenty-four-hour urinary protein excretions on days 3 and 19 of pregnancy were presented. There were no difference among the three groups on day 3 of pregnancy ( p > 0.05), but on day 19 of pregnancy, after BML-111 administration, this level (0.41 ± 0.06 mg/24 hours) was significantly lower than in the Cd group (0.79 ± 0.07 mg/24 hours, n = 8, *** p < 0.001). All data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
