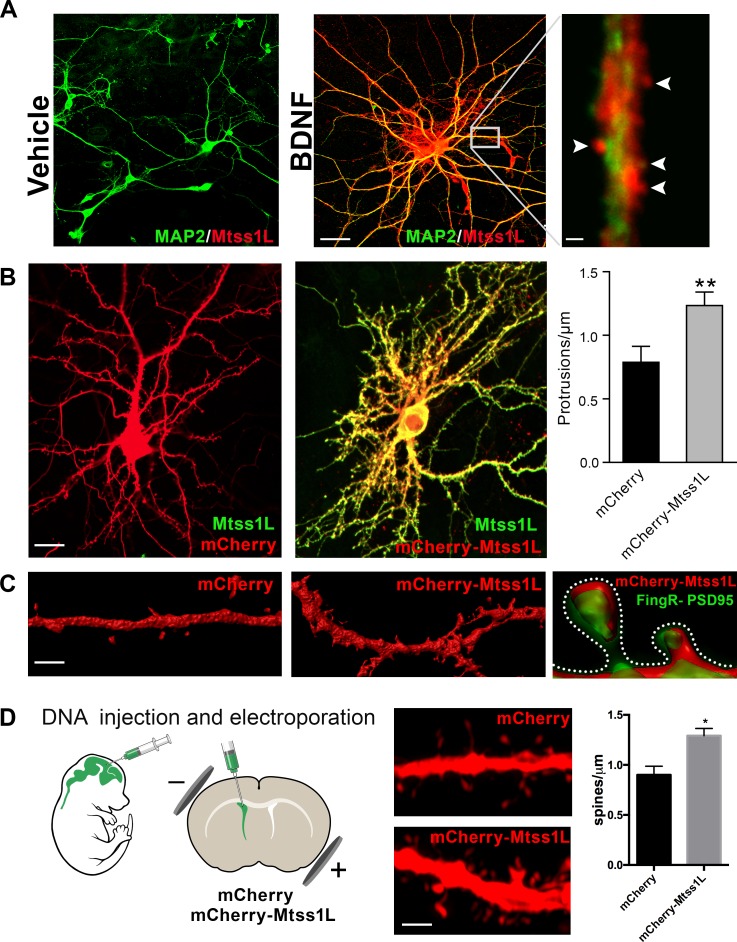
Figure 5. Induced Mtss1L expression in vitro and in vivo.
(A) Primary hippocampal neurons were cultured with or without BDNF from DIV 7–14 to examine activity-dependence of Mtss1L expression. Representative images of hippocampal neurons co-stained with anti-Mtss1L (red) and the somatodendritic marker anti-MAP2 (green) showed robust Mtss1L immunoreactivity in BDNF-treated cells (middle), but not in the vehicle-treated controls (left). Scale bar: 20 µm. High magnification image of a single dendrite in a BDNF-treated neuron showed localization of Mtss1L (red) in dendritic shaft and spines (right, arrowheads, scale bar: 1.5 µm). (B) Representative images of cultured hippocampal neurons transfected with mCherry or Mtss1L-mCherry and stained with anti-Mtss1L (green). Scale bar: 12 µm. Ectopic expression of Mtss1L markedly increased the number of dendritic protrusions (mCherry: 0.9 ± 0.09, Mtss1L-mCherry: 1.3 ± 0.07, unpaired t-test, p=0.004, n = 3). (C) Higher magnification images of dendritic segments from hippocampal neurons transfected with mCherry (left) or Mtss1L-mCherry (middle) shows the increased number of protrusions. Scale bar: 3 µm. Merged image at right of PSD-95.FingR-GFP and Mtss1L-mCherry in co-transfected neurons demonstrates that the protrusions contained postsynaptic proteins. Scale bar: 0.5 µm. (D) DNA solution was injected into the lateral ventricle of P0 pups followed by gene delivery by electroporation. Representative dendritic segments of dentate granule cells expressing control plasmid mCherry (top) or mCherry-Mtss1L (bottom) 21 days post-electroporation. Scale bar: 3 µm. Mtss1L-mCherry expressing cells show increased dendritic protrusions in vivo (mCherry, 0.9 ± 0.03, n = 3, Mtss1L-mCherry, 1.3 ± 0.07, n = 3, unpaired t-test, p=0.004).
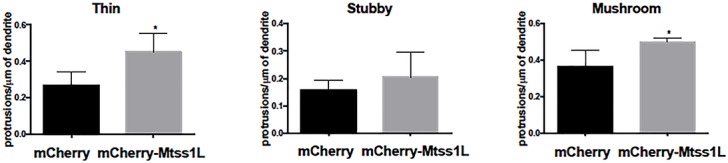
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Effect of Mtss1L overexpression on dendritic spine subtypes of primary hippocampal neurons in vitro.