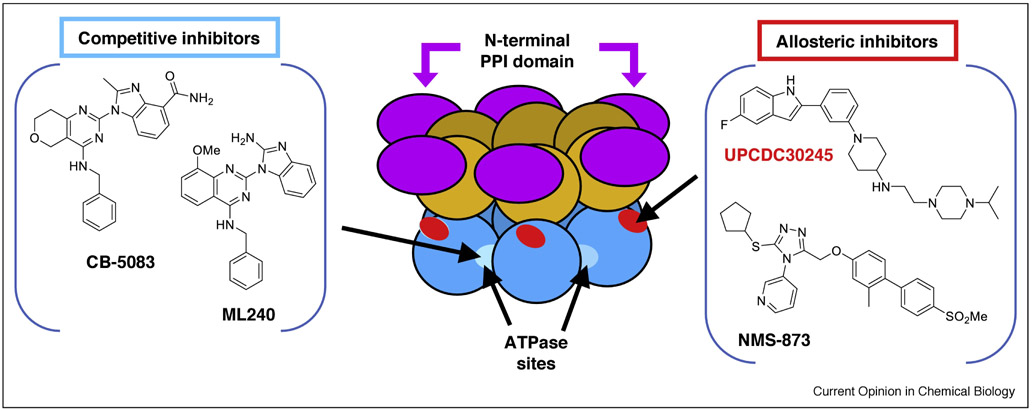
Figure 3. Examples of p97 small molecule inhibitors.
The center cartoon shows the domain structure of p97, with arrows pointing to the binding sites for allosteric and ATP-competitive inhibitors. Each monomer in the p97 hexamer has three folded domains: the N-terminal PPI domain (purple), the D1 ATPase domain (orange), and the D2 ATPase domain (blue). Competitive inhibitors ML240 and CB5083 (left panel) bind at the ATP-binding pocket of p97 D2 domain (light blue). Inhibitors UPCDC30245 and NMS-873 (right panel) bind at allosteric sites in the D2 ATPase domain, near the D1-D2 linker region (red). The binding site for allosteric inhibitors has been defined by cross-linking, resistant mutants, and cryo-EM. See references in the main text.