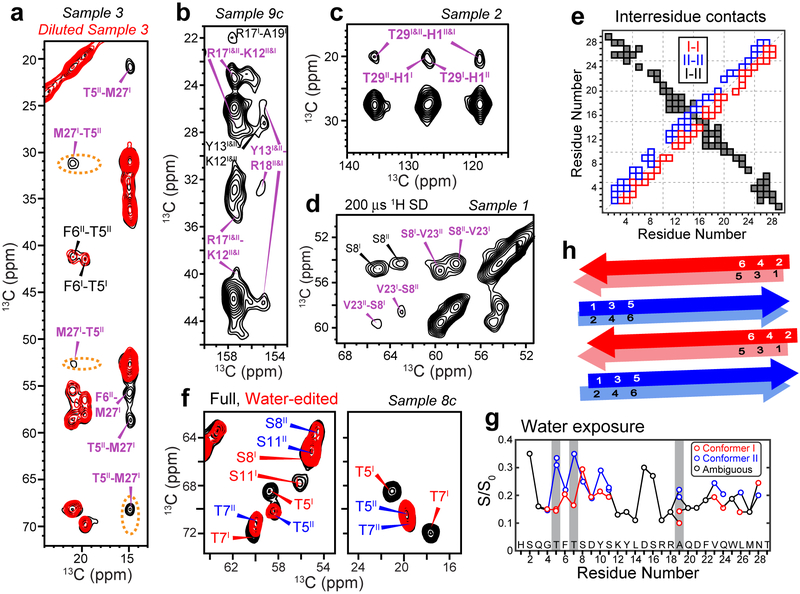
Figure 3.
2D NMR spectra indicate that glucagon forms antiparallel β-sheets with two distinct steric zipper interfaces. a, 500 ms 13C SD spectra of sample 3 without or with dilution. M27-T5 and M27-F6 cross peaks are observed, whose intensities decrease significantly upon dilution of the labeled peptide with unlabeled peptide, supporting antiparallel packing of conformers I and II. b, 500 ms 13C SD spectra of sample 9c. Y13-R18 correlations indicate cation-π interaction. c, 500 ms 13C SD spectra of sample 2 show H1–T29 cross peaks, indicating that the two termini of the peptide come into close proximity. d, 200 μs CHHC spectrum of sample 1. Strong V23-S8 Cα-Cα cross peaks indicate that the antiparallel packing is along the hydrogen-bonded fibril axis. e, Summary of measured inter-residue correlations. Conformer I – I correlations are shown below the diagonal, whereas conformer II – II correlations are shown above the diagonal. These sequential contacts contain both intramolecular and intermolecular contributions and are shown as open squares. The unambiguously intermolecular conformer I – conformer II contacts are shown as black squares, with the x-axis indicating conformer I and the y-axis indicating conformer II. f, Full and water-edited 2D spectra of sample 8c. Residues T5, T7, and S11 are well hydrated in conformer II but dehydrated in conformer I, indicating that the water-accessible surfaces differ between the two conformers. g, Intensity ratios between the water-edited spectra and full spectra, showing relative water accessibility of the sidechains. Even-numbered residues are more hydrated (high S/S0 values) in conformer I whereas odd-numbered residues are more hydrated in conformer II. h, Schematic of the glucagon β-strand packing. The fibrils contain two distinct β-strands that hydrogen-bond in antiparallel along the fibril axis. The two strands in each homodimer cross section have C2 symmetry around an axis parallel to the peptide backbone.