Fig. 1. Memory B cells rapidly migrate into the FRT upon secondary challenge in immunized mice.
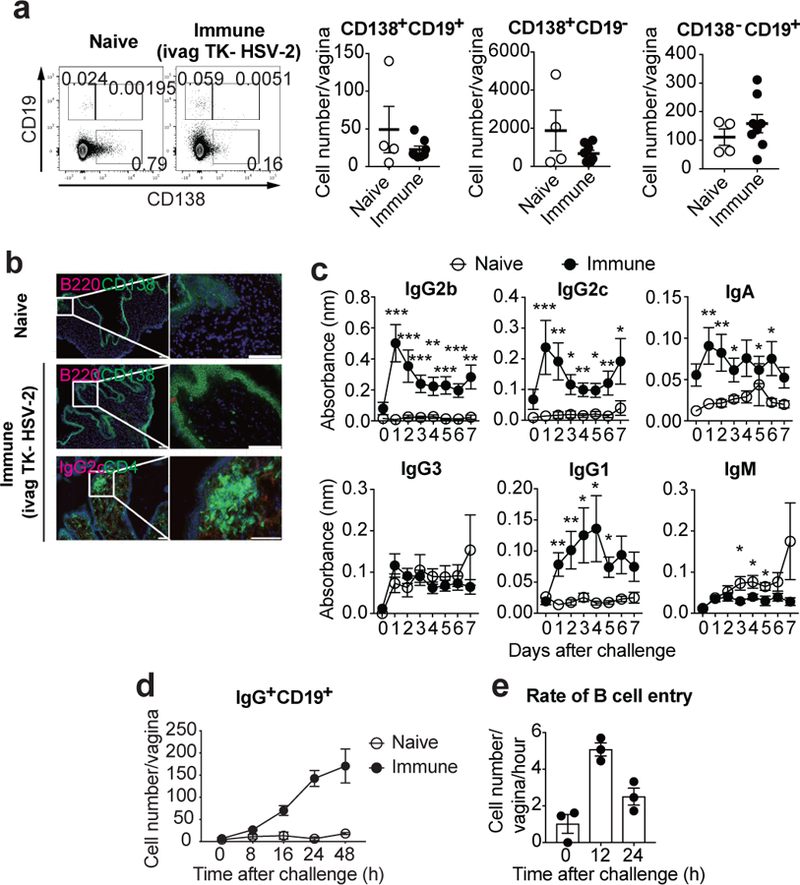
a-b, C57BL/6 mice were immunized intravaginally with TK− HSV-2. a, Five weeks later, CD138+CD19+, CD138+CD19−, and CD138−CD19+ cells in vaginal tissues were analyzed in both naïve (n=4) and immunized (n=8) mice by flow cytometry. b, Six weeks later, frozen sections of vagina were stained with antibodies against CD138 and CD4 (green), B220 and IgG2c (red), and DAPI (blue). Scale bars indicate 100 μm. c–d, C57BL/6 mice with or without immunization with TK− HSV-2 five weeks prior were challenged with WT HSV-2 intravaginally. c, Following challenge, HSV-2-specific antibodies in vaginal wash were measured by ELISA (naïve; n=9, immune; n=13). Sample dilution was 1:7. d, After challenge, the number of B cells in vagina was analyzed by flow cytometry (naïve; n=3, immune; n=4). e, B cells isolated from DsRed mice immunized with TK− HSV-2 five weeks prior were adoptively transferred into mice immunized with TK− HSV-2 five weeks prior at the indicated hours after secondary challenge with WT HSV-2. Vaginal tissues were collected 2 h after adoptive transfer, and the number of DsRed+IgG+ B cells in vaginal tissues was analyzed by flow cytometry (n=3). Data are mean ± SEM. Data are pooled from two (a) and four (c) independent experiments, or are representative of three (b,d) and two (e) independent experiments. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001 (two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test).
