Fig. 4. CD4 TRM cells play essential role for recruitment of memory B cells upon secondary challenge in immunized mice.
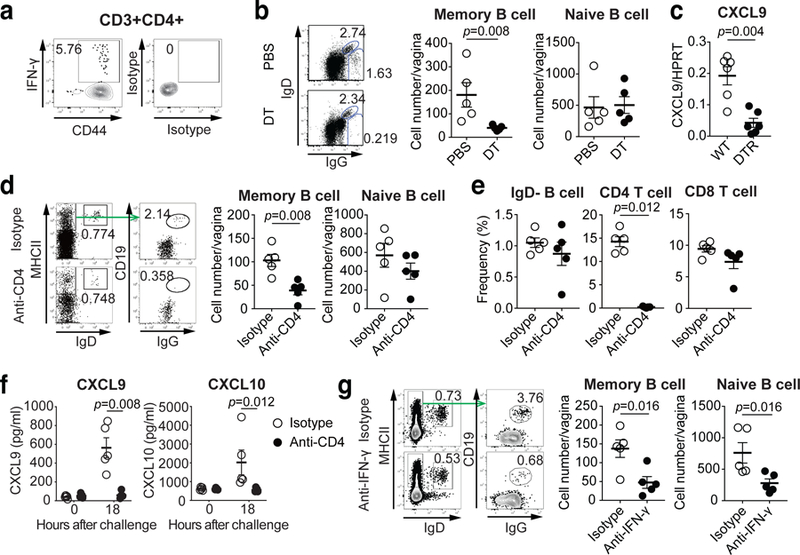
a, C57BL/6 mice were immunized intravaginally with TK− HSV-2. Five weeks later, HSV-2-specific IFN-γ+ CD44+CD4+ T cells in the vagina were analyzed by flow cytometry. b-c, CD11bDTR BM chimeric mice were immunized intravaginally with TK− HSV-2. b, Eight weeks later, these mice were treated with DT to deplete CD11b+ macrophages and challenged with WT HSV-2. One day later, the number of IgD+ naive B cells and IgG+ memory B cells in vaginal tissues was analyzed by flow cytometry (n=5). c, Five weeks after immunization, DT-treated chimeric mice were challenged with WT HSV-2. Eight hours later, mRNA expression of CXCL9 in vaginal tissue were measured by real-time qPCR (n=6). d-f, C57BL/6 mice were immunized intravaginally with TK− HSV-2. Five weeks later, mice were treated with anti-CD4 antibody to deplete CD4 T cells. d, One day after challenge with WT HSV-2, the number of IgD+ naive B cells and IgG+ memory B cells in vaginal tissues was analyzed by flow cytometry (n=5). e, The numbers of circulating memory B cells, CD4 T cells and CD8 T cells in blood after CD4 depletion were analyzed by flow cytometry (n=5). f, Eighteen hours after challenge, the level of CXCL9 and CXCL10 chemokines in vaginal wash was measured by ELISA (n=5). g, C57BL/6 mice immunized intravaginally with TK− HSV-2 were treated with anti-IFN-γ antibody. One day after challenge with WT HSV-2, the number of IgD+ naive B cells and IgG+ memory B cells in vaginal tissues was analyzed by flow cytometry (n=5). Data are mean ± SEM (two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test). Data are representative of two (a–c,g) and three (d–f) independent experiments.
