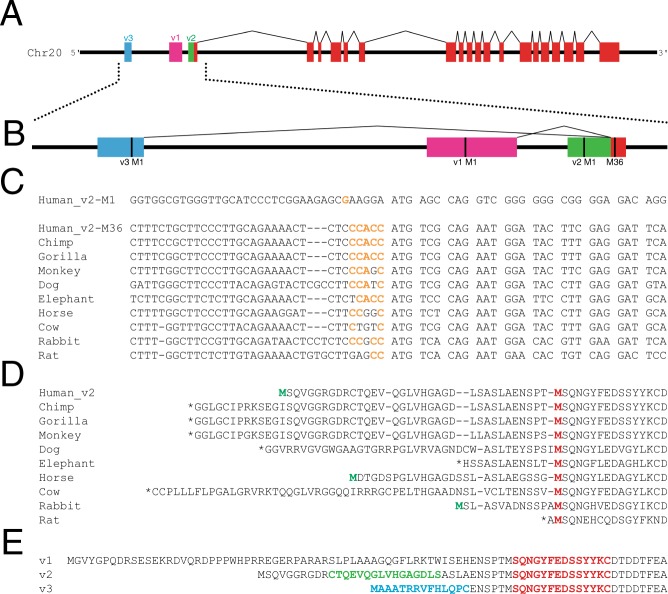
Figure 1.
Bioinformatic analysis of human SLC4A11. (A) cDNA sequences of known human SLC4A11 transcripts were mapped onto a 15 kb segment of Human chromosome 20 genomic DNA to show transcript structure (coloured boxes), connected by introns (black lines). Each transcript variant (v1, v2 and v3) has a unique starting exon which results in unique N-terminal regions of the predicted protein and a common core region (red). (B) Magnified view of the 5′ end of the SLC4A11 gene. Each variant has a predicted start codon (M1; vertical black line). M36 (numbering based on predicted sequence of v2) marks the start of the common coding sequence for all transcripts. (C) Alignment of DNA sequences surrounding the predicted start codons in SLC4A11 v2 for multiple species. Kozak translational start sequence efficiency40 is indicated with bases matching the consensus shown in orange. For human SLC4A11, Kozak analysis is indicated for v2 start at Met 1 and 36 (v2-M1 and v2-M36). (D) Alignment of amino acid sequences for v2 SLC4A11 for the indicated mammals. Red Methionine (M) residue indicates the position corresponding to human v2-M36. Green Met indicates in frame Met upstream of v2-M36. Stop codons are indicated (*). (E) Amino acid sequences of SLC4A11 v1-v3 are aligned with sequences of peptides used to generate splice form-selective antibodies highlighted in red: SLC4A11-common, green: SLC4A11-v2-M1 and blue: SLC4A11-v3.