Figure 2.
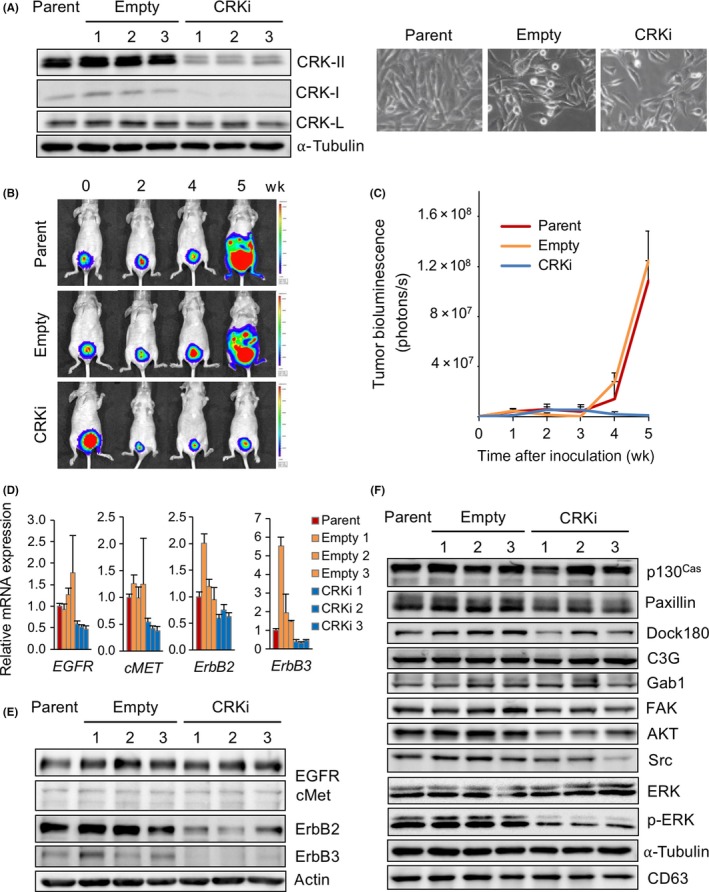
Depletion of CRK decreases expression of ErbB2 and ErbB3 in bladder cancer cells and abolishes metastasis of bladder cancer in vivo. A, Establishment of CRK knockdown bladder cancer cells. UM‐UC‐3 cells were stably transfected with expression plasmids producing shRNA targeting CRK (CRKi) or its control vector (Empty). Cell lysates of parent, control (Empty), and CRK knockdown cells (CRKi) were subjected to immunoblotting with anti‐CRK and CRK‐L Abs. α‐Tubulin was used as a loading control. Photomicrographs of the cells were obtained under bright‐field illumination (right panels). B,C, tdTomato‐luc2‐labeled UM‐UC‐3 cells (parent, empty, and CRKi) were injected into the bladder muscle layer in athymic mice (n = 4, each group). Tumor growth was measured weekly using the IVIS Spectrum imaging system (B) and graphed as the mean ± SD (C). In CRKi cell‐injected mice, metastasis to the liver and lung was absent. D, Total RNAs were isolated from UM‐UC‐3 cells (parent, empty, and CRKi), and endogenous expression levels of EGFR,cMET, ErbB2, and ErbB3 mRNAs were analyzed by quantitative RT‐PCR. E,F, Levels of expression and phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), cMET, ErbB2, and ErbB3 (E) and CRK‐related signaling molecules (F) were examined by immunoblotting
