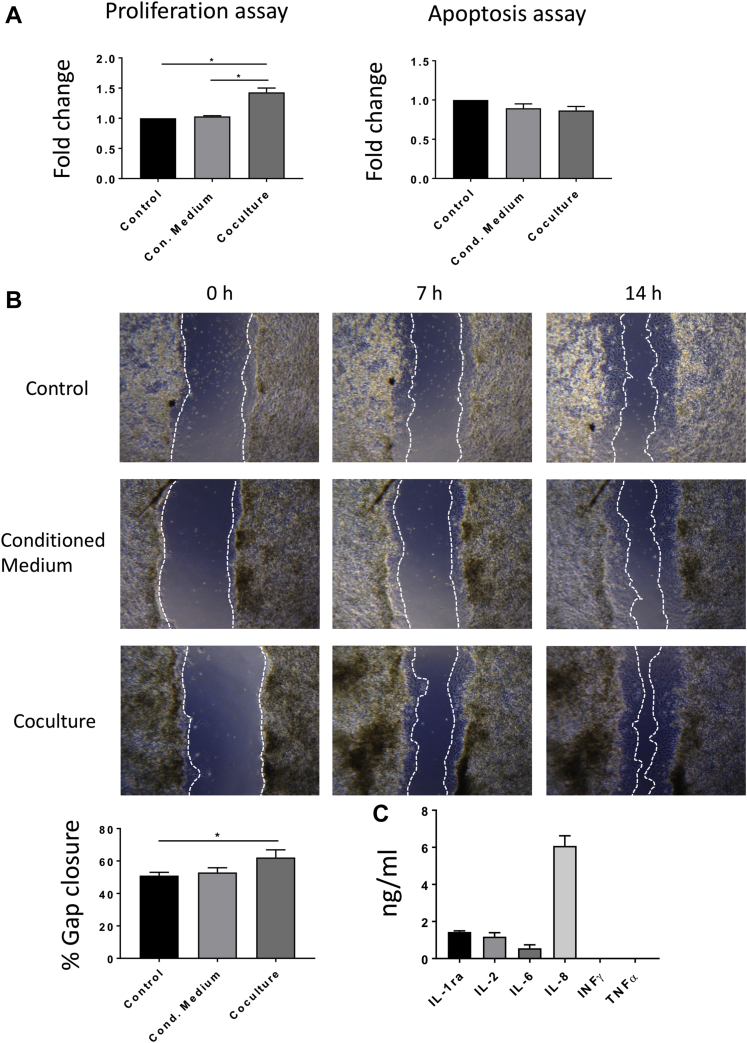
Figure 8.
in Vitro Assessment of the Paracrine Effect of the Thymus-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
(A) Evaluation of the proliferation and apoptosis of rat cardiomyocytes (rCMs) cultured in the presence of thymus-derived mesenchymal stem cells (T-MSCs) or with their conditioned medium showed that the presence of the stem cells stimulates the proliferation of the cardiomyocytes (CMs), without affecting apoptosis (n = 3). (B) A migration assay of the rCMs either cultured with the conditioned medium or cocultured with the T-MSCs demonstrated that the stem cells can promote the migration of the CMs. The proportion of gap closure 14 h following the scratch was greater in the cocultured condition compared with the control. (C) Analysis of the cytokines and growth factors released by the T-MSCs showed secretion of interleukin (IL)–1ra, IL-2, and IL-6 and a high level of IL-8. Absence of interferon (INF)-γ and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–α was observed in the porcine T-MSC (pT-MSC)–conditioned medium.