-
A
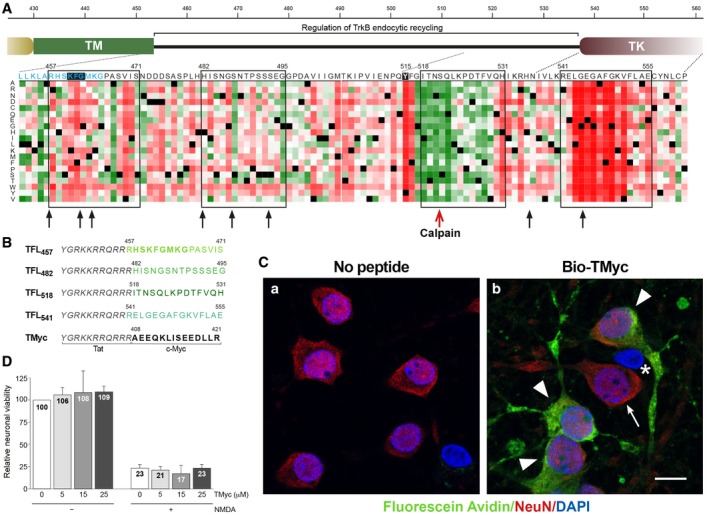
Region details and sequence selection. Common residues to TrkB‐FL and TrkB‐T1 are in light blue and include a KFG sequence completely conserved in Trk proteins (filled black box). In the heatmap representation, dark red, white, and green represent, respectively, strong, weak, or no effect of point mutations, while black corresponds to wild‐type residues. Black arrows denote theoretical calpain cleavage sites, while the red arrow points an experimentally established site. Sequences included in CPPs are emphasized by black rectangles. TM, transmembrane; TK, tyrosine kinase.
-
B
CPP design. Peptides contain Tat aa 47–57 (italic) followed by the indicated rat TrkB‐FL (green) or c‐Myc (black) sequences.
-
C
Confirmation of peptide entry into neurons. Cultures were incubated with Bio‐TMyc (25 μM, 1 h) (image b) or left untreated (image a). Arrowheads highlight peptide permeability, detected by Fluorescein Avidin D (green), into neurons labeled with neuronal‐specific antibody NeuN (red). Peptide is not detected in some neurons (arrow) and non‐neuronal cells (asterisk). Confocal microscopy images correspond to single sections and are representative of five independent experiments. Scale bar, 10 μm.
-
D
Effect of TMyc on neuronal survival. Primary cultures were incubated with TMyc (5, 15, or 25 μM, 30 min) and subjected to treatment with NMDA (100 μM) and glycine (10 μM) for 4 h. Specific neuronal viability was established and expressed relative to values in cultures with no treatment. Means ± SEM are represented (n = 8), and statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA test followed by post hoc Tukey's HSD test.