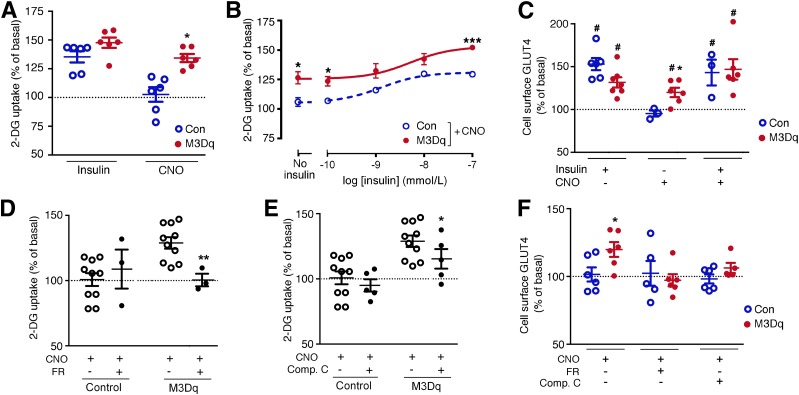
Figure 1.
Activation of a Gq-linked designer GPCR (M3Dq) promotes glucose uptake and GLUT4 translocation in vitro. A–F: Functional studies were carried out with L6-GLUT4myc myoblasts expressing either M3Dq or GFP (control [Con]). A and B: [3H]2-DG uptake was studied following incubation of L6-GLUT4myc cells with either insulin (100 nmol/L) or CNO (10 μmol/L), as described in detail in research design and methods. In B, CNO (10 μmol/L) stimulation of [3H]2-DG uptake was measured in the presence of increasing insulin concentrations. C: CNO (10 μmol/L) promotes the translocation of GLUT4 to the cell surface of M3Dq-L6GLUT4myc myoblasts. GLUT4 cell surface expression was determined using a FACS-based approach, as described in research design and methods. D: CNO-induced (10 μmol/L) stimulation of [3H]2-DG uptake in M3Dq-L6-GLUT4myc myoblasts is completely abolished by FR900359 (FR; 1 μmol/L), a selective inhibitor of Gq/11. E: CNO-mediated (10 μmol/L) enhancement of [3H]2-DG uptake in M3Dq-L6GLUT4myc myoblasts is greatly reduced in the presence of compound C (Comp. C; 10 μmol/L), an AMPK inhibitor. F: CNO-induced (10 μmol/L) translocation of GLUT4 to the cell surface of M3Dq-L6GLUT4myc myoblasts is abolished in the presence of FR (1 μmol/L) or Comp. C (10 μmol/L). Data are expressed as means ± SEM of six (A–C and F), three (D), or seven (E) independent experiments, each performed in duplicate or triplicate. All responses were expressed relative to baseline responses (set equal to 100%) obtained in the absence of drugs. Basal [3H]2-DG uptake values were similar (P = 0.13) between M3Dq-expressing and GFP control cells (62,375 ± 1,531 and 73,786 ± 5,862 dpm/mg protein, respectively). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. control (Student t test); #P < 0.05 as compared with baseline (100%; no drug treatment; one-sample t test).