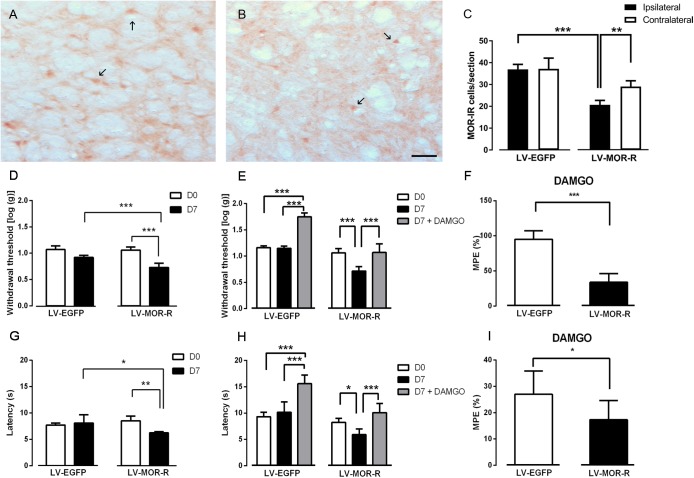
FIGURE 3.
Lentiviral-mediated MOR knockdown at the DRt increases mechanical and thermal sensitivity in naïve animals. Representative photomicrographs of MOR-immunoreactive (IR) cells at the DRt of naïve animals injected with LV-EGFP (A) and LV-MOR-R (B). Typical MOR immunolabeling is marked by arrows. Scale bar in (B): 100 μm (A is at the same magnification). Data in (C) represents the number of MOR immunoreactive (IR) cells after lentiviral vectors injection into the DRt at the injected (ipsilateral) and contralateral side. LV-EGFP (n = 6) or LV-MOR-R (n = 5) were injected at the DRt and their effects were assessed before (D0) and 7 days (D7) after injection by the von Frey (D) and hot-plate (G) which evaluate mechanical and thermal sensitivity, respectively. An additional group of animals injected with LV-EGFP (n = 6) or LV-MOR-R (n = 7) into the DRt, was administrated 0,1 ng of DAMGO at the DRt. The effects of DAMGO were assessed before (D7) and 15 min after injection (D7+DAMGO) by the von Frey (E) and hot-plate (H). Data in (F) and (I) represents the effects of DAMGO converted to percent maximum possible effect (%MPE) on the von Frey and hot-plate tests, respectively. Data are presented as mean ± SD.∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.