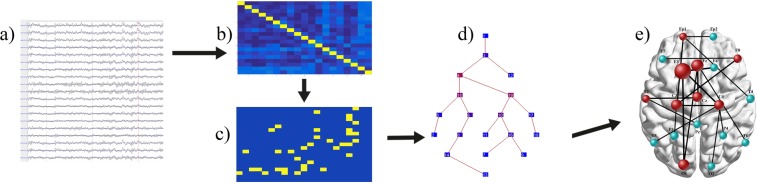
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of MST-networks formation from the resting-state EEG recordings: (a) selection of thirty EEG artifacts-free epochs, each containing 4096 samples (approximately 8 seconds per epoch) from each participants, (b) computation of the functional connectivity matrices based on phase lag index (PLI) for every selected EEG epochs for each possible electrodes pairs, in every frequency band, (c) minimum spanning tree (MST) matrix calculation, based on previously obtained PLI matrices for all frequencies, (d) the MST graph reconstruction, being an output from the Brainwave software, (e) illustrative reconstruction of topological distribution of hubs and leaf nodes posted on a simplified cortical surface, created from averaged MST matrix in a given frequency band. Network was reconstructed keeping the rule of generating loop-less connections between the nodes. Analyses and computations depicted in points (a–d) were performed for each individual participant, while the topological network reconstruction (point e) has been prepared for groups, to show a qualitative model of networks with the approximate neuronal location of hubs, leaf nodes and connections.