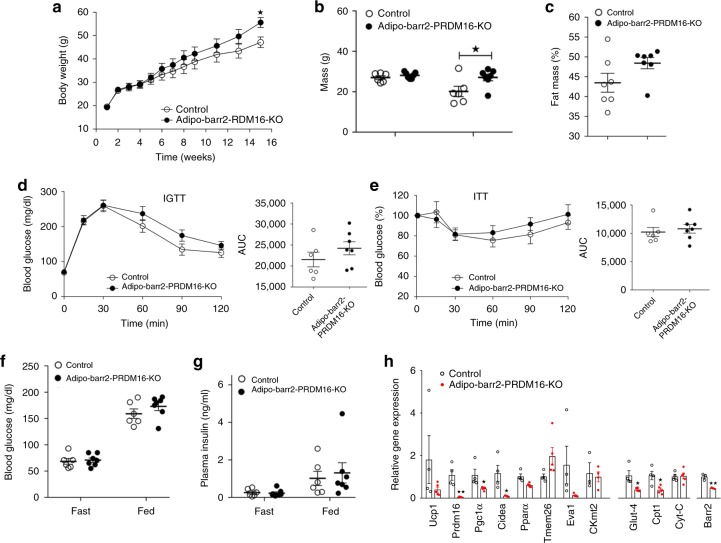
Fig. 6.
The beneficial metabolic effects displayed by adipo-barr2-KO mice are absent in barr2-PRDM16 double KO mice. a Body weights of control mice (genotype: barr2 f/f Prdm16 f/f) and adipo-barr2-PRDM16 double KO mice (genotype: adipoq-Cre barr2 f/f Prdm16 f/f) maintained on a HFD after 4 weeks of age (n = 6 or 7 per group). b, c Body composition (b) and fat mass (% of body weight) (c) of the indicated mouse strains maintained on a HFD for 15 weeks. d, e IGTT (1 g glucose/kg i.p) (d) and ITT (0.75 U insulin /kg i.p.) (e). Mice were maintained on a HFD for 8–9 weeks (n = 6 or 7 per group). AUC, area under the curve. f, g Freely fed and fasting blood glucose (f) and plasma insulin levels (g) in mice maintained on a HFD for 10 weeks (n = 6 or 7 per group). h Relative transcript levels of browning/beiging marker genes and other key metabolic genes, including barr2, determined by qRT-PCR analysis of iWAT RNA after 16 weeks of HFD feeding (n = 4 per group). Male mice were used for all studies. Data are expressed as means ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (a two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test; b, c, f–h two-tailed Student’s t-test)