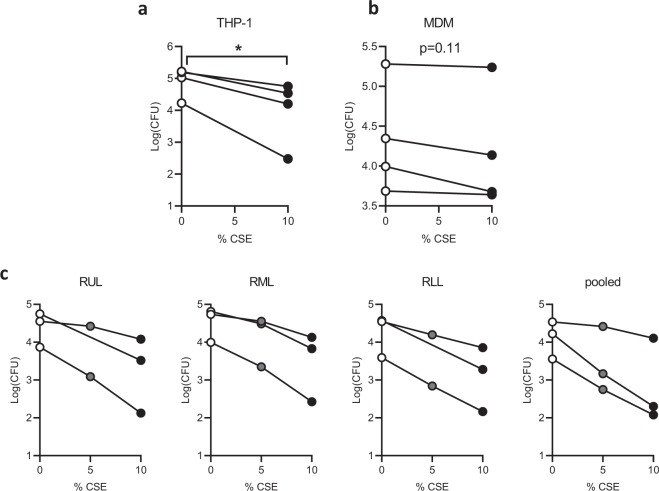
Figure 1.
CSE inhibits phagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by immortalized and primary macrophages. (a) THP-1 cells were treated with 50 nM PMA for 48 hours to differentiate into macrophages, then phagocytosis was quantified by a gentamicin protection assay. Cells were cultured in standard medium without antibiotics, pre-treated with 10% CSE or media vehicle for 20 min, then infected with log-phase P. aeruginosa at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10 for 20 min. They were then washed and 10x gentamicin was added to kill extracellular bacteria. Three additional washes were performed and cells were lysed in 0.1% triton X-100 in PBS. Colony forming units (CFU) were quantified on LB agar plates and CFU per million macrophages was calculated, log(mean CFU) for four individual experiments are graphed with lines connecting replicates from an individual experiment. *p < 0.05 by paired t-test (b) Primary human peripheral blood monocytes were differentiated into monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM) by treatment for 7 days with 100 ng/mL M-CSF, followed by a gentamicin protection assay as in a. Means of triplicate technical replicates from four independent experiments (separate donors) are graphed. (c) Primary alveolar macrophages (AMΦ) were purified from right upper lobe (RUL), right middle lobe (RML), or RLL (RLL) bronchoalveolar lavage, followed by phagocytosis assays after pretreatment with vehicle, 5% CSE or 10% CSE (5% point was omitted from RUL and RLL replicates of one donor due to limited cell number). Means of triplicate technical replicates from three separate donors are graphed. CSE significantly reduced phagocytosis (p < 10−15) based on a linear model of log10 CFU as a function of CSE concentration, experimental batch and location in the lung.