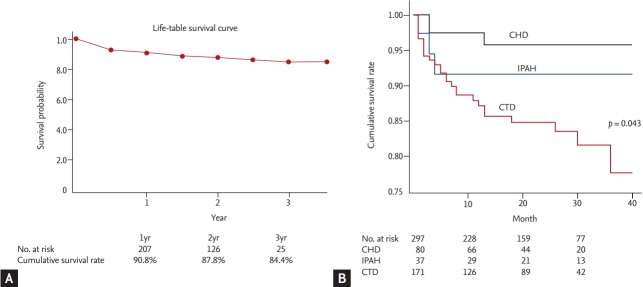
Figure 1.
Cumulative survival and comparison of survival among etiologies. (A) Cumulative survival curve of the incident cases in the Korean Registry of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (KORPAH; n = 297). The 1st-, 2nd- and 3rd-year estimated survival rates were 90.8%, 87.8%, and 84.4%, respectively. (B) Comparison of survival according to the etiologies of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) of the incident cases in the KORPAH (n = 297). This figure presents a comparison of prognoses according to the etiologies of PAH. PAH with connective tissue disease (CTD) corresponded to the highest mortality (18.8%), followed by idiopathic PAH (IPAH) (8.1%), and PAH with congenital heart disease (CHD; 3.9%) (p = 0.043).