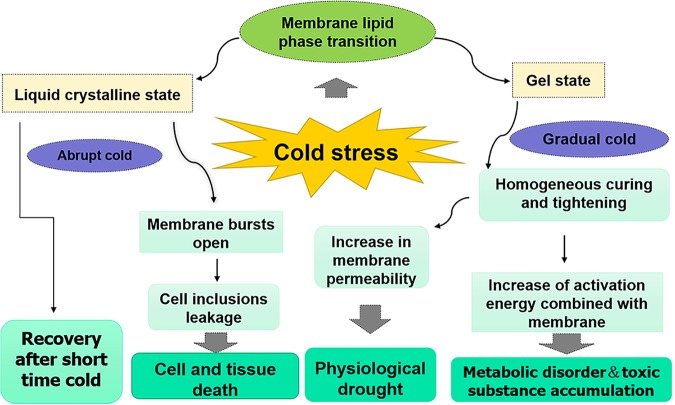
FIGURE 2.
Effects of cold stress on membrane permeability. The main reason for the increase of membrane permeability in plants under cold stress is the phase transition of membrane lipids. When plants encounter an abrupt cold, membrane lipid is in liquid crystalline state, cold tolerant plants can recover in a short time, but the electrolyte leakage caused by membrane bursts open will happen in cold sensitive plants and ultimately lead to cell and tissue death. When plants encounter a gradual cold, membrane lipid is in gel state, the permeability of membrane increases with the prolongation of cold time, resulting in the loss of intracellular water and physiological drought. At the meantime, the increased activation energy of enzymes bound to membrane leads to metabolic disorder and toxic substance accumulation in plants.