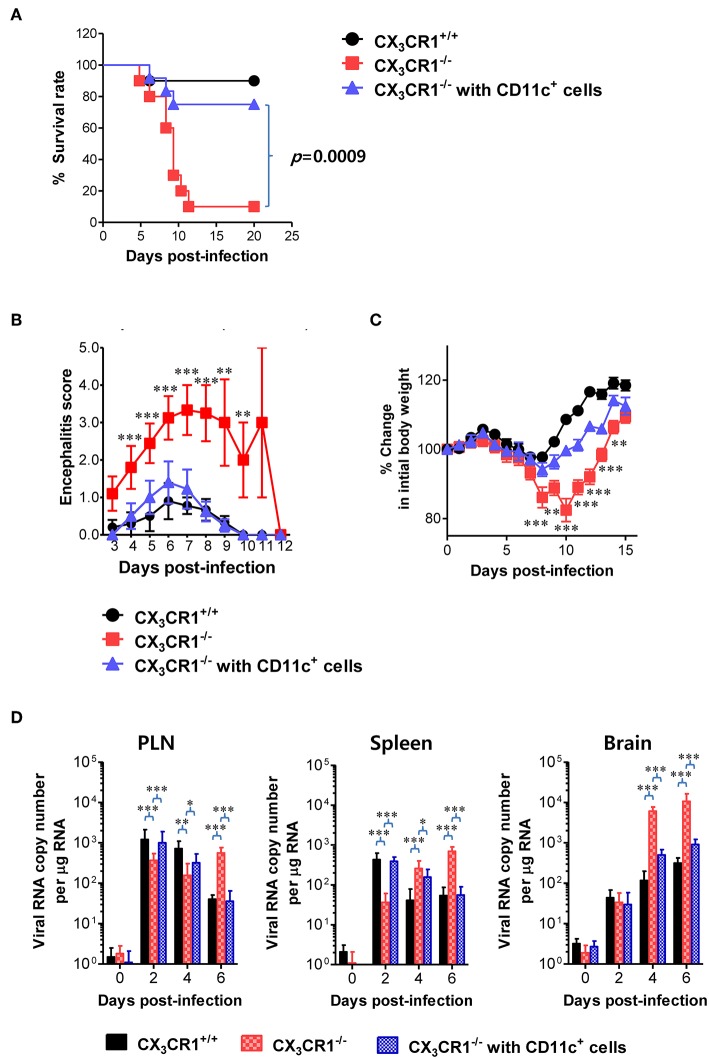
Figure 9.
Restoration of resistance to JE by adoptive transfer of CX3CR1+ DCs. CX3CR1+CD11c+ DCs from spleens of wild-type mice were sorted and adoptively transferred into CX3CR1−/− mice via tail vein and foot pad inoculation (5 × 105 cells/mouse). CX3CR1−/− recipients (n = 10–11) were subsequently infected with JEV (5.0 × 107 PFU) via footpad inoculation. CX3CR1+/+ wild-type mice and CX3CR1−/− mice that received no cells were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. (A) Susceptibility of CX3CR1−/− recipients for CX3CR1+CD11c+ DCs to JE. The proportion of surviving mice in each group was monitored daily for 20 days. (B) Encephalitis score. Mice infected with JEV were scored for encephalitis from 3 to 12 dpi and the encephalitis score was expressed as the average score ± SEM of each group. (C) Changes in body weight. Changes in body weight were expressed as average percentage ± SEM of body weight relative to the time of challenge. (D) Viral burden in peripheral lymphoid and CNS tissues of CX3CR1−/− recipients for CX3CR1+CD11c+ DCs during JE progression. The viral burdens in spleen, brain, and spinal cord of CX3CR1−/− recipients infected with JEV were assessed by real-time qRT-PCR at indicated dpi. Viral RNA load was expressed as viral RNA copy number per microgram of total RNA. Data show the average ± SEM of levels derived from at least three independent experiments (n = 4–5). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; and ***p < 0.001 comparing CX3CR1−/− mice and CX3CR1−/− recipients of CD11c+ DC at indicated dpi.