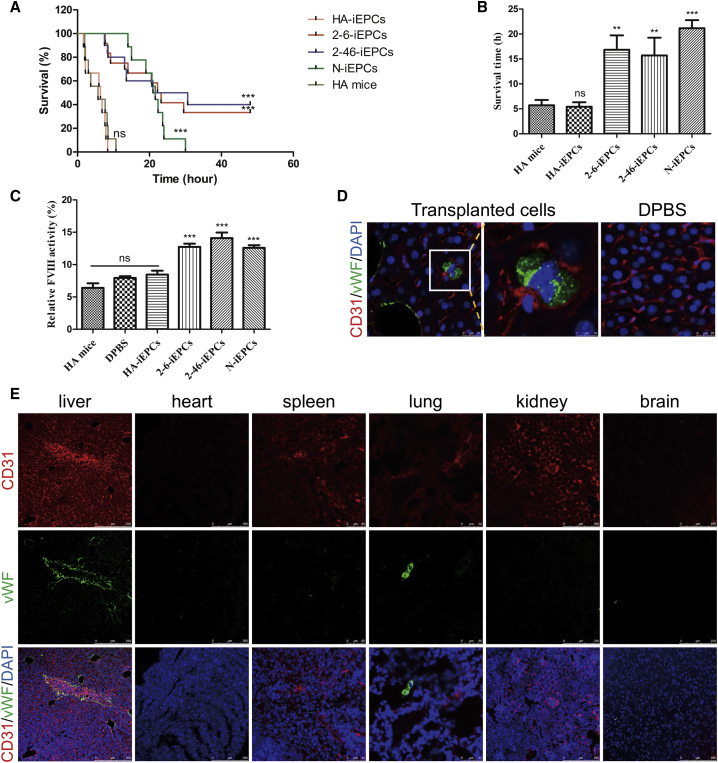
Figure 5.
Functional Rescue of FVIII Deficiency in HA Mice by C-iEPCs
(A) Proportions of surviving mice after the tail-clip challenge. HA mice, mice with hemophilia A (n = 9); HA-iEPCs, mice with hemophilia A, receiving transplanted cells derived from HA-iPSCs (n = 9); 2-6-iEPCs, mice with hemophilia A, receiving transplanted cells derived from 2-6-iPSCs (n = 12); 2-46-iEPCs, mice with hemophilia A, receiving transplanted cells derived from 2-46-iPSCs (n = 10); N-iEPCs, mice with hemophilia A, receiving transplanted cells derived from N-iPSCs (n = 9). ns, not significant compared with HA mice; ***p < 0.001 compared with the HA-iEPC group (log-rank test). (B) Average survival time of mice after the tail-clip challenge. Notably, 4 of the 12 HA mice that received 2-6-iEPC transplants and 4 of the 10 HA mice that received 2-46-iEPC transplants and survived the challenge were excluded from this analysis. Bars represent the mean ± SEM; ns, not significant compared with HA mice. ***p < 0.001 and **p < 0.01 compared with the HA-iEPCs. (C) Relative FVIII activity was determined in plasma from HA mice with no transplant (n = 6) and HA mice with a transplant of Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (DPBS) (n = 6), HA-iEPCs (n = 6), N-iEPCs (n = 8), or C-iEPCs (2-6-iEPCs and 2-46-iEPCs) (n = 8). Bars represent the mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001 compared with HA-iEPCs. (D) Livers of HA mice with 2-46-iEPCs that survived the tail-clip challenge were collected and analyzed using tissue immunofluorescence with an anti-human vWF antibody, and the results indicated that the transplanted human cells homed to the mouse liver. No signal was detected in the negative control (DPBS) group. CD31 (red); vWF (green). DAPI was used for nuclear staining. (E) Tissue immunofluorescence analysis of main organs of mice with 2-46-iEPCs, showing that anti-human vWF-positive cells were detected in the livers and lungs, but not in the spleens, hearts, kidneys, or brains. CD31 (red); vWF (green). DAPI was used for nuclear staining.