Figure 1.
Aspirin Treatment Inhibits the EMT and Promotes miR-203 Expression in EBV-Positive Cells
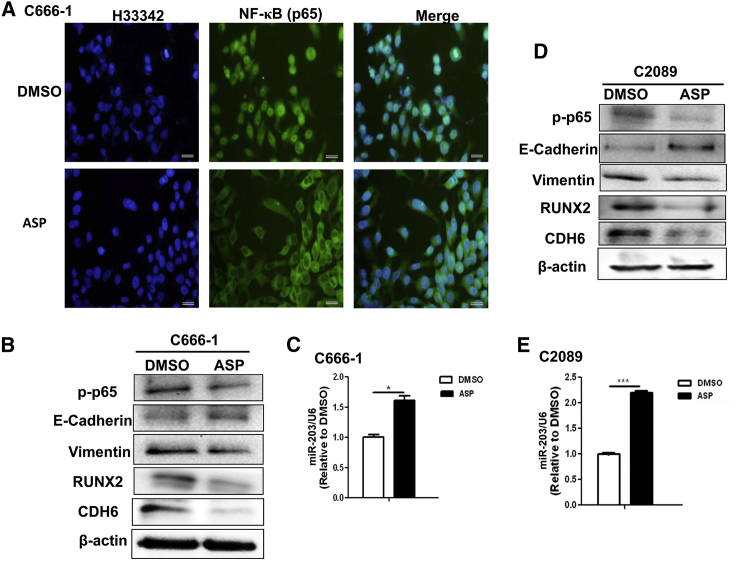
(A) Representative images showing that aspirin (ASP) treatment inhibited the activation and nuclear entry of NF-κB (p65). An IF assay was used for p65 detection. Scale bars, 50 μm. (B) The detection of the EMT markers phosphorylated p65 (p-p65), RUNX2, and CDH6 in NPC C666-1 cells by WB at 36 h after ASP treatment. E-cadherin is an epithelial marker and vimentin is a mesenchymal marker. (C) The detection of miR-203 expression level in C666-1 cells by qPCR. (D) The detection of the EMT markers p-p65, RUNX2, and CDH6 in C2089 cells by WB following ASP treatment. (E) The detection of miR-203 in C2089 cells by qPCR. The results are the means ± SD from three independent experiments (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.