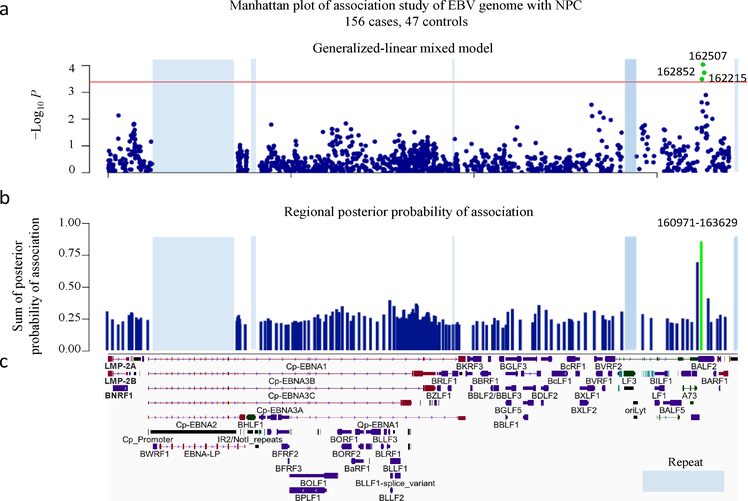
Figure 2. Genome-wide association analysis of EBV variants in 156 NPC cases and 47 controls.
(a) Manhattan plot of genome-wide P values from the association analysis using a generalized-linear mixed model. The −log10-transformed P values (y axis) of 1545 variants in 156 NPC cases and 47 controls are presented according to their positions in the EBV genome. The minimum P value (SNP 162507C>T) is 9.17×10−5. The red line is the suggestive genome-wide significance P value threshold of 4.07×10−4. The three SNPs 162507C>T, 162852G>T and 162215C>A reaching genome-wide significance are labeled as green. (b) The regional plot of the posterior probabilities of association. The EBV genome was partitioned into overlapping 20-variant bins with 10-variant overlap between adjacent bins. The sum of the posterior probabilities for variants was assigned to each region. The one region from position 160971 to 163629 with strong evidence (> 0.85) for association with NPC risk is shown in green. (c) Schematic of EBV genes. Repetitive regions in EBV genomes are masked by light blue.