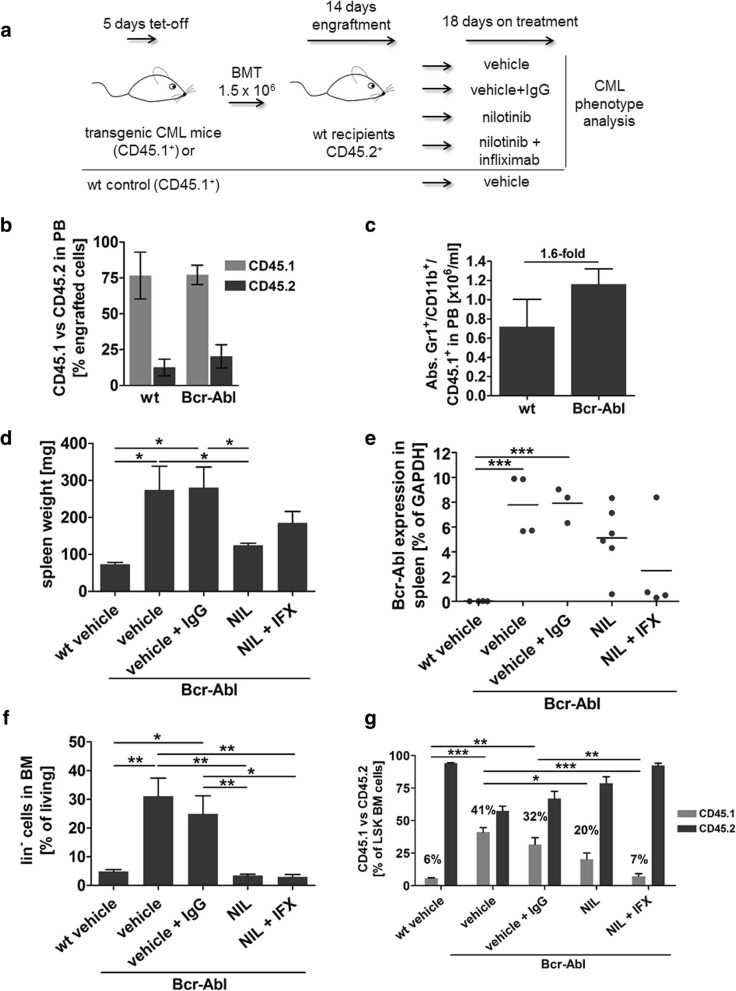
Fig. 3.
Anti-inflammatory therapy and Bcr-Abl inhibition reduces leukemic stem cells in vivo. a Experimental design for the treatment of Bcr-Abl and wt (CD45.1) BM transplanted recipient FVB/N mice (CD45.2). b Engraftment of CD45.1+ donor cells in the peripheral blood of Bcr-Abl and wt transplanted mice was evaluated by FACS 14 d after BMT (n = 3/3). c Absolute Gr-1+/ CD11b+/ CD45.1+ cell number of wt and Bcr-Abl transplanted recipients in peripheral blood 14 d after BMT (n = 3/3). d Upon autopsy spleen weight of FVB/N wt and FVB/N Bcr-Abl transplanted recipients with the indicated treatment was determined. e Bcr-Abl mRNA expression was analyzed in spleen cells of recipient mice by qRT-PCR. f FACS analysis of lin− cell population of FVB/N wt and FVB/N Bcr-Abl transplanted recipients which received the indicated therapy. g Distribution of donor (CD45.1) and recipient (CD45.2) derived cells within the LSK (lin−, c-kit+, Sca-1+) cell compartment of transplanted mice with the indicated treatments. (n = 4/ 4/ 3/ 6/ 4, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001)