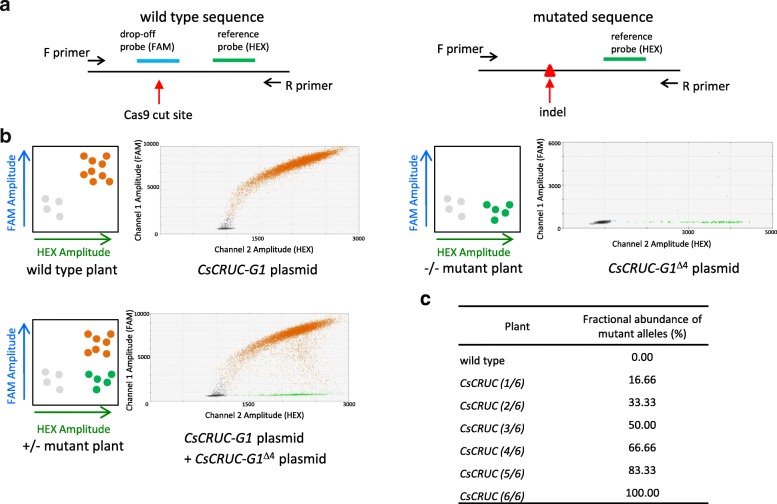
Fig. 2.
Overview and validation of ddPCR drop-off assay to detect CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutations. a Schematic of probe and primer configuration for detection of mutations. Both the drop-off probe (FAM) and reference probe (HEX) bind to the same amplicons derived from wild-type sequences. Sequence polymorphisms prevent binding of the drop-off probe and only the reference probe binds to amplicons with mutations at the Cas9 cut site. b Schematic of anticipated drop-off assay outcome represented on a 2-D fluorescence intensity plot and results using synthesized CsCRUC-G1 plasmid template. Wild type plants or CsCRUC-G1 plasmid generate amplicons in which both drop-off probe and reference probe bind, generating only double-positive (HEX and FAM) droplets. Mutant plants with no wild-type sequence or CsCRUC-G1Δ4 plasmid containing a four base pair deletion at the predicted Cas9 cut site generate amplicons in which only the reference probe binds, resulting in only single-positive (HEX) droplets. Plants with wild-type sequence and mutated sequence or a mixture of CsCRUC-G1 plasmid and CsCRUC-G1Δ4 plasmid generate wild-type amplicons in which both drop-off probe and reference probe bind, generating double-positive droplets, and mutation-containing amplicons in which only the reference probe binds, generating single-positive droplets. c Expected fractional abundance of drop-off probe events vs. reference probe events representing when heritable mutations have occurred in one to six alleles of CsCRUC