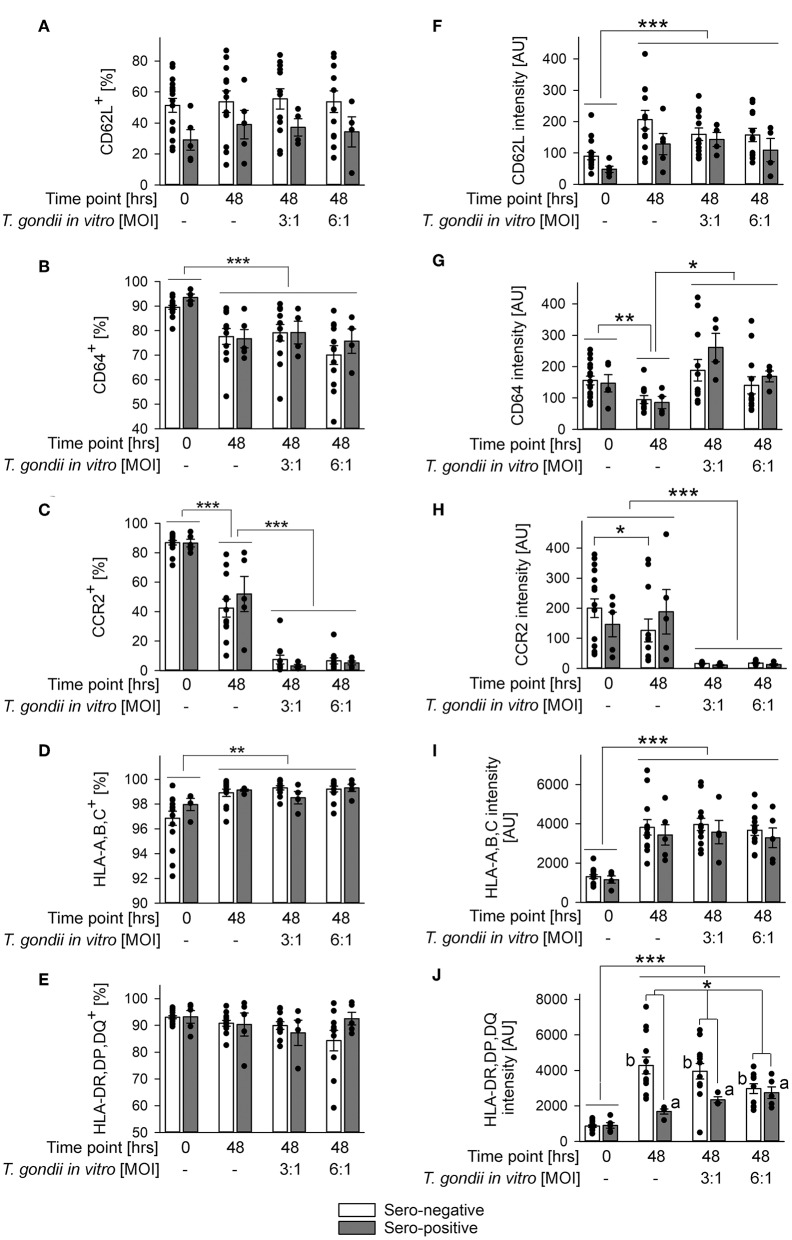
Figure 4.
Impact of in vitro infection of monocyte-enriched PBMCs with T. gondii on expression of CD62L, CD64, CCR2, HLA-A,B,C, or HLA-DR,DP,DQ on monocytes from donors with or without chronic toxoplasmosis. Monocyte-enriched PBMCs were isolated from blood samples and were either directly FACS-analyzed (0 h) or were cultivated in vitro for 48 h and infected or not with T. gondii during the final 24 h as indicated and then FACS-analyzed. Expression of cell surface markers was determined for CD14-positive monocytes as outlined in Figure 2. (A–E) Percentages of cells from T. gondii seropositive (gray bars) or seronegative (open bars) individuals with expression of surface markers above background staining. (F–J) Expression levels of surface markers as indicated on monocytes from T. gondii seropositive or seronegative blood donors. Data represent means ± S.E.M. from 5 T. gondii seropositive and from 13 out of 16 seronegative blood donors which had been randomly selected for in vitro infection assays; outlyers were excluded. Individual data points are also indicated. Significant differences between groups were identified by ANOVA [***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05; a and b indicate dose-dependent increase or decrease, respectively, of HLA-DR,DP,DQ after parasite infection (p < 0.01)].