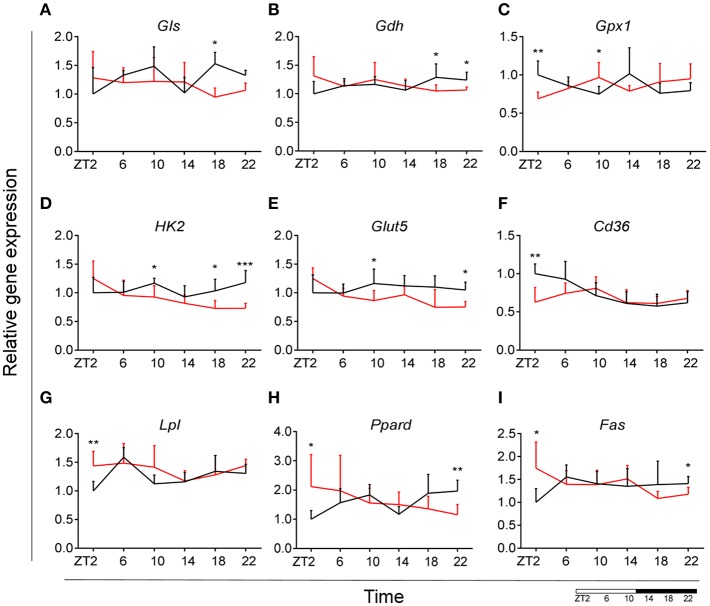
Figure 5.
HFD effect on glutamate, glucose and lipid microglial metabolism in rats. Relative gene expression of (top) glutamate substrate utilization genes Gls (A) and Gdh (B), as well as antioxidant enzyme gene Gpx1 (C); (middle) glucose metabolism genes Hk2 (D) and Glut5 (E), fatty acid sensing gene Cd36 (F); (bottom) fatty acid sensing genes Lpl (G) and Ppard (H), as well as fatty acid synthesis gene Fas (I) in HFD-fed rats (red) compared to Chow-fed controls (black) evaluated at six time points, starting at ZT2. Data are presented as means ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined using Two-way ANOVA effect for Interaction, Diet, and Time (ZT); Student t-test is used for diet effect within a separate time point (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). Scale (bottom right) represents light (ZT0-12) and dark (ZT12-24) phase.