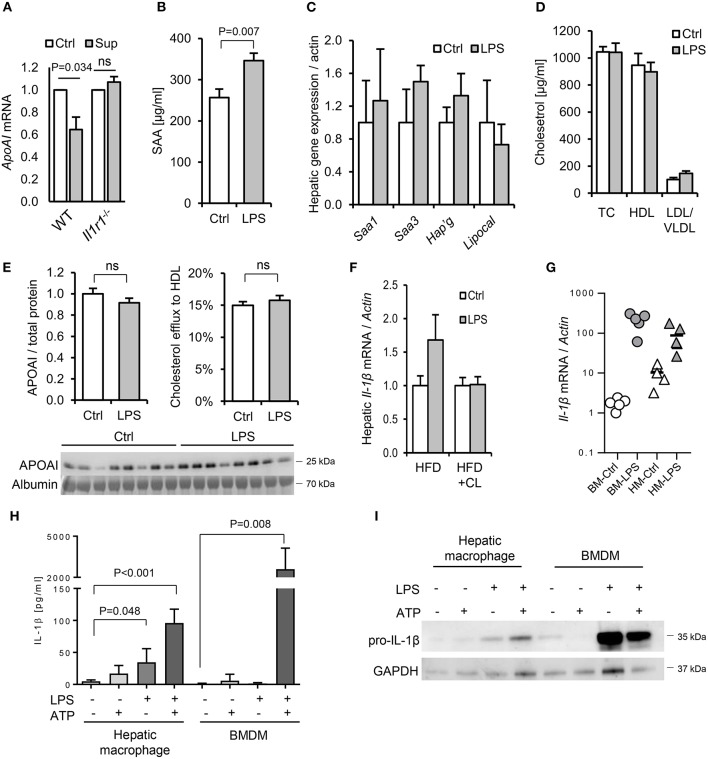
Figure 10.
Interleukin-1 is a key mediator of the lipid and acute phase responses to ingested LPS in vivo. (A) ApoAI mRNA responses of isolated wild-type (WT) and interleukin-1 receptor deficient (Il1r1−/−) hepatocytes to conditioned medium of LPS-treated WT hepatic macrophages. (B–D) Plasma serum amyloid A (SAA), lipoprotein cholesterol and hepatic acute phase response (APR) mRNA responses in HFD-primed Il1r1−/− mice 24 h after oral gavage with saline alone (Ctrl) or 1 mg E. coli LPS (n = 8, 10/gp). (E) ApoAI protein and efflux capacity in sera of the same mice. (F) Hepatic IL-1β mRNA in LPS-gavaged HFD-primed WT mice treated (or not) with clodronate liposomes (CL). (G) IL-1β mRNA in LPS-treated isolated primary mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) and hepatic macrophages (HM). (H) Secreted and (I), cytosolic IL-1β protein production by LPS and ATP-stimulated primary mouse BMDM and hepatic macrophages (n = 3–5/gp). P-values vs. Ctrl, ANOVA with Dunnett's test.