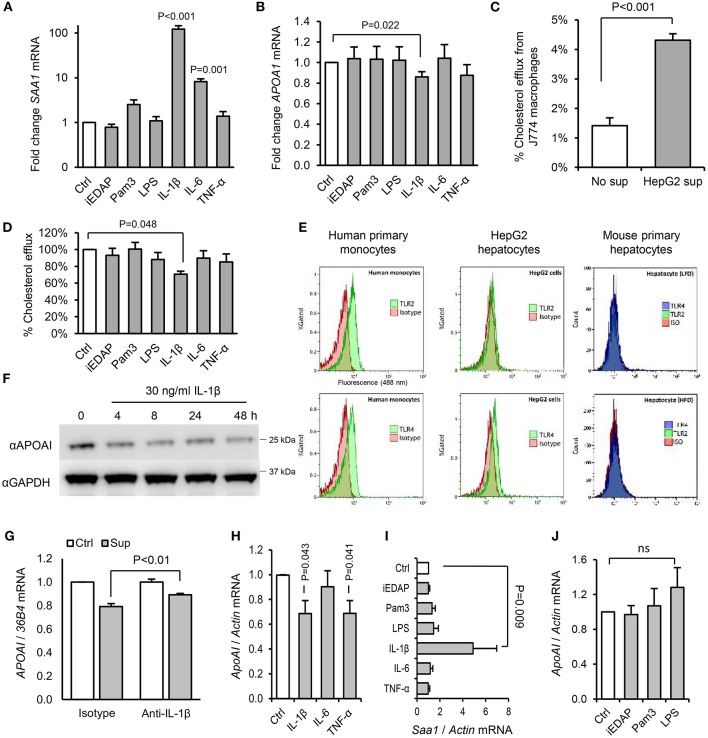
Figure 9.
Interleukin-1β plays a key role in the downregulation of RCT mediators by hepatocytes in response to products secreted by activated hepatic macrophages. (A,B) Human HepG2 hepatocytes increased serum amyloid A (SAA)-1, and reduced ApoAI, mRNA expression significantly in response to IL-1β, but not stimulants of NOD1 (iEDAP), TLR2 (Pam3CSK4), or TLR4 (E. coli LPS). (C) Conditioned medium of HepG2 cells significantly increased the efflux of 3H-radiolabelled cholesterol from J774 macrophages. (D) The capacity of conditioned media of HepG2 hepatocytes to accept 3H-radiolabelled cholesterol effluxed from J774 macrophages was reduced significantly by IL-1β, but not by IL-6, TNF-α, or stimulants of NOD1, TLR2, or TLR4. (E) Flow cytometry showed abundant surface TLR2 and TLR4 on human primary monocytes, but no TLR2 and little TLR4 on HepG2 hepatocytes. Murine primary hepatocytes isolated by hepatic perfusion also showed no expression of TLR2 or TLR4, in low-fat diet (LFD) or high-fat diet (HFD)-primed mice (representative of 4 experiments). (F) Kinetics of ApoAI protein expression in HepG2 cells treated with IL-1β determined by Western blot. (G) HepG2 ApoAI mRNA response to conditioned medium of LPS-treated human monocytes with isotype-control or IL-1β neutralizing antibody (n = 5 exps). (H,I) ApoAI and SAA1 mRNA responses of primary hepatocytes (isolated from n = 6 LFD-fed mice) to inflammatory cytokines (20 ng/ml). (J) ApoAI mRNA responses of primary hepatocytes (n = 3 HFD-primed mice) to indicated PAMPs (100 ng/ml). Error bars shown are SEM. P-values vs. control condition, Student's T-tests or ANOVA with Dunnett's test.