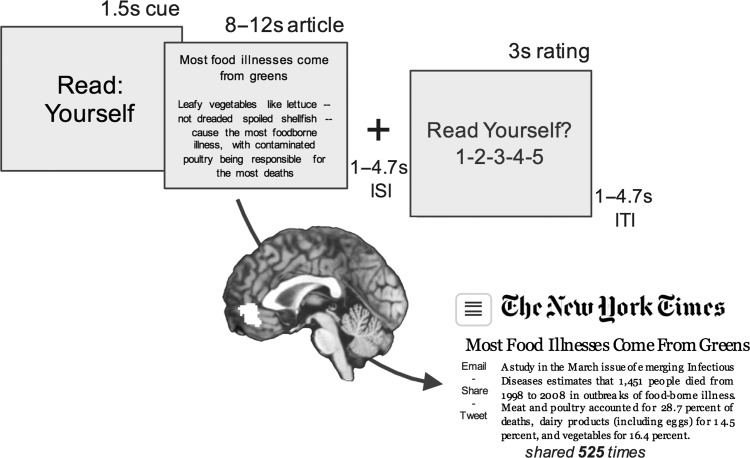
Figure 1.
In-scanner New York Times article viewing task and tracking of population information sharing. Brain activity was measured as people read and listened to headlines and abstracts of New York Times articles focusing on health and fitness. Population-level counts of the number of times each article was shared online within the first 30 days after publication (via email or social media) were collected from the New York Times website. Multilevel models used brain responses from the viewing task to as a predictor variable, and counts of population article sharing as an outcome variable.