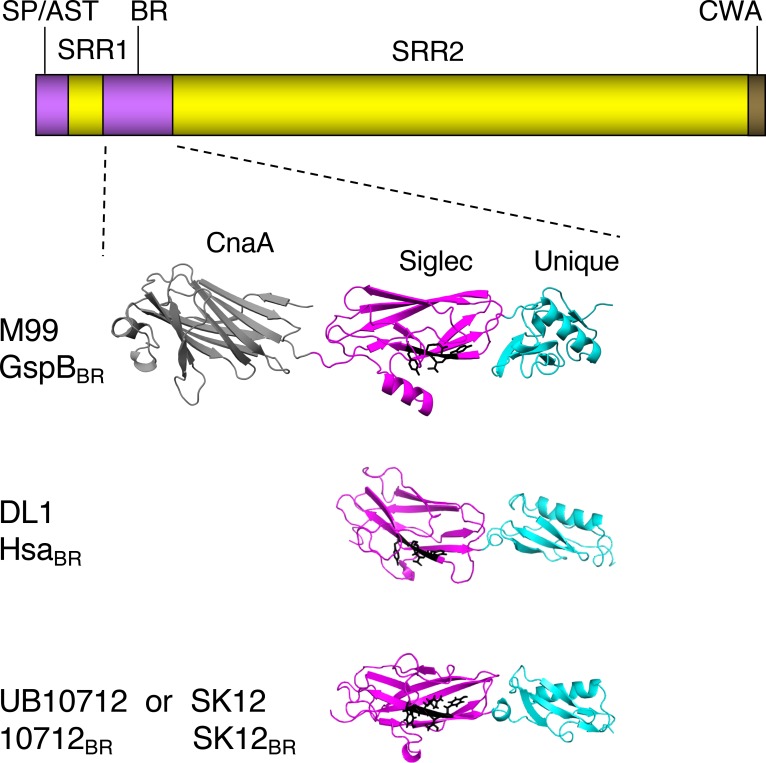
Fig 1. Comparison of the GspB, Hsa and 10712 BRs.
The upper diagram shows the general domain organization of the SRR glycoproteins. SP/AST, signal peptide and accessory Sec transport domain; BR, ligand binding region; CWA, cell wall anchor. The SRR1 and SRR2 regions undergo glycosylation in the bacterial cytoplasm, prior to transport by the accessory Sec system. The lower portion shows high-resolution crystal structures of the binding regions of GspB, Hsa and the SRR glycoprotein from the S. gordonii strain UB10712. The GspBBR structure was reported previously [30]. Partially refined structures of the HsaBR and 10712BR were provided by T. Iverson (manuscript submitted; PDB files 6EFC and 6EFF pending release). Note that the GenBank entry for the 10712BR sequence originally listed the source strain as Streptococcus mitis NCTC10712 (GenBank JYGN00000000) [66]. The S. gordonii SK12 BR sequence is identical to that of UB10712, and was obtained by translation of the publicly available partially assembled SK12 genome (NZ_LAWP01000015). The CnaA domain is found in some Siglec-like BRs but does not contribute to sialoglycan binding. The sialoglycan ligand preferences thus far appear to be dictated by the Siglec domains. The YTRY motif residues are shown as black sticks. The Unique domain may modulate the conformation of the Siglec domain.