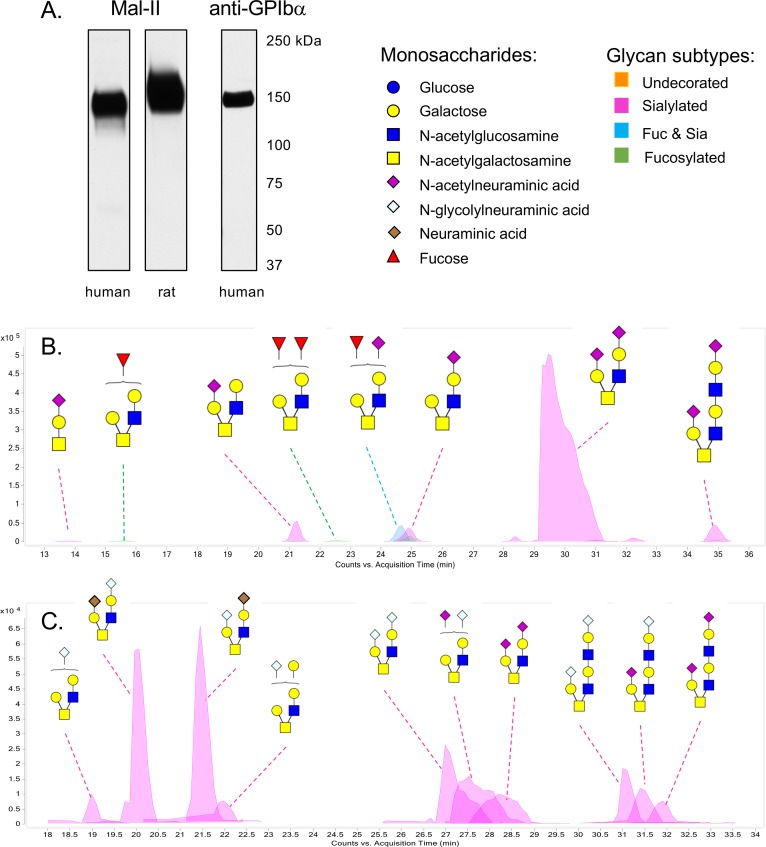
Fig 8. Comparison of human and rat platelet GPIbα O-glycans.
A: Western and lectin blot analysis showing GPIbα as the major sialylated glycoprotein in the crude platelet extracts. Lanes contain 2 μl of the GPIbα preparations. Proteins were separated by electrophoresis on 3–8% polyacrylamide, transferred to nitrocellulose, and then probed as indicated. Mal-II is a lectin commonly used to detect α2–3 sialic acids, and is specific for sTa and di-sialylated T-antigen [68]. The anti-GPIbα antibody is specific for the human protein. An antibody that recognizes the rat homolog in western blots is not currently available. B: Putative structures of the O-glycans released from the human GPIbα sample. The structures are based on the precise masses and inferred monosaccharide composition (Table 4) in addition to the MS/MS fragmentation patterns. Brackets indicate cases where the position of monosaccharides could not be assigned. Monosaccharide symbols follow the Symbol Nomenclature for Glycans system [67]. C: Putative structures of the O-glycans released from the rat GPIbα sample. The structures are based on the precise masses and inferred monosaccharide composition (Table 5) in addition to MS/MS fragmentation data. Brackets indicate cases where the position of monosaccharides could not be assigned.