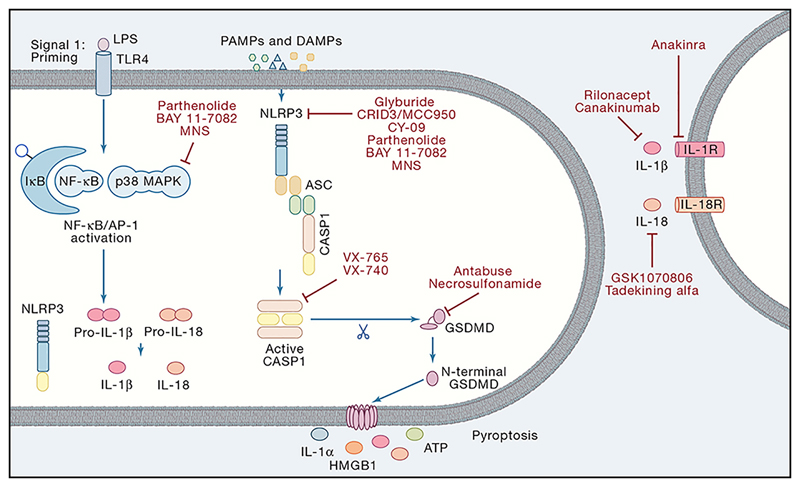
Figure 4. Therapeutic targets in the inflammasome pathways.
To date, several inhibitors have been described for the NLRP3 inflammasome. Parthenolide, BAY 11-7082 and 3,4-methylenedioxy-β-nitrostyrene (MNS) are known to inhibit both NF-κB signalling and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Additionally, specific inhibition of NLRP3 has been reported by studies using glyburide and its derivative CRID3/MCC950. Also, CY-09 has been described as a NLRP3 specific inhibitor. More downstream, both caspase-1 and gasdermin D have been targeted by several compounds. Belnacasan (VX-765) and Pralnacasan (VX-740) are bioavailable prodrugs of a potent inhibitor for caspase-1. Alternatively, Antabuse and necrosulfonamide (NSA) were reported to block cleavage and/or oligomerisation of Gsdmd thereby preventing pyroptosis. Once released, the mature IL-1β and IL-18 signal through its appropriate receptors to initiate inflammation in neighbouring cells. Also, anti-cytokine therapies have been generated. Anakinra is recombinant IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) thereby preventing IL-1 signalling. Canakinumab is a fully human monoclonal anti-IL-1β antibody directed against human IL-1β. Finally, the extracellular domains of both receptors (IL-1R1 and IL-1RAcP) were made into a fusion protein as a soluble decoy receptor (Rilonacept). Alternatively, two IL-18 targeted therapeutics have been described. GSK1070806 is a neutralizing humanized monoclonal antibody and Tadekinig alfa is recombinant human IL-18BP both involved in captured bio-active IL-18 away from its receptor.