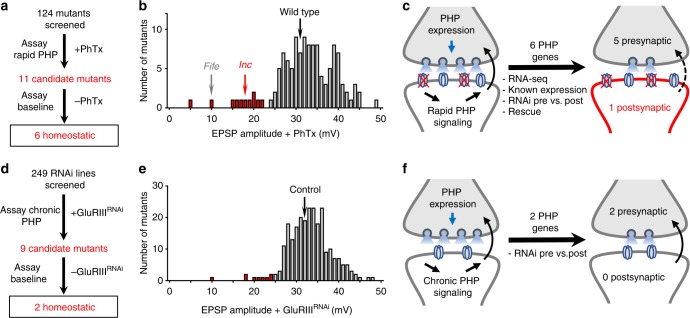
Fig. 1.
Forward genetic screens identify six genes necessary for PHP in distinct synaptic compartments. a and d Electrophysiology-based forward genetic screening strategy and outcomes for the PhTx (a) and GluRIII knock down (d) approaches. b and e Average EPSP amplitudes of each mutant or RNAi line screened following PhTx application (b) or GluRIII knock down (e). In wild-type controls, inhibition of glutamate receptors results in reduced mEPSP amplitude, as expected. However, EPSP amplitude remains similar to baseline values due to a homeostatic increase in presynaptic neurotransmitter release (quantal content). Highlighted in red are all mutants that showed EPSP values > two standard deviations below controls. c and f Schematic illustrating the determination of pre- and postsynaptic functions for the positive hits from the screens. See Supplementary Data 1 for detailed information about all genes screened and additional data