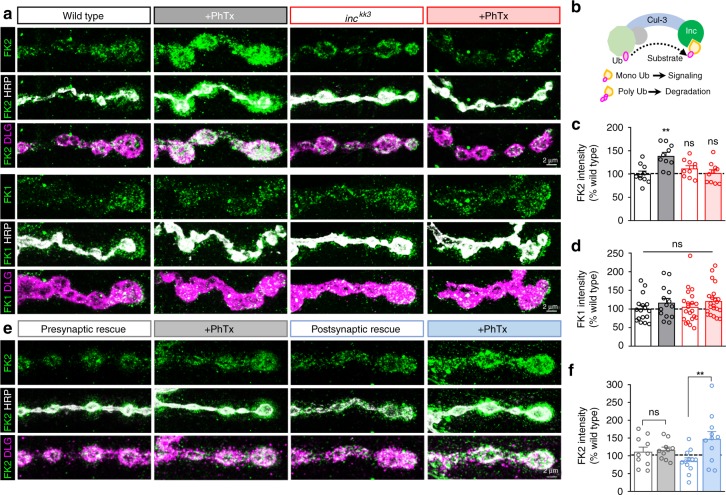
Fig. 5.
inc is required for rapid mono-ubiquitination at postsynaptic compartments following glutamate receptor perturbation. a Representative NMJ images from wild-type and inc mutants immunostained with anti-FK2 (mono- and poly-ubiquitin) or anti-FK1 (poly-ubiquitin only), -HRP and -DLG, before and after PhTx application. At wild-type NMJs, the FK2 signal rapidly increases at postsynaptic densities after PhTx application (indicated by the signal outside of HRP), while no change is observed in the FK1 signal. However, no change in either FK2 or FK1 intensity is observed at baseline or after PhTx application in inc mutant NMJs. b Schematic illustrating the Cul3 ubiqutin ligase complex, where Inc serves as an adaptor to target substrates for either mono-ubiquitination (which can confer signaling functions) or poly-ubiquitination (which leads to proteasomal degradation). Quantification of average FK2 (c) and FK1 (d) immunointensity levels after PhTx application in the indicated genotypes normalized to wild type (–PhTx: wild type, n = 10 (FK2), n = 17 (FK1); inckk3, n = 10 (FK2), n = 21 (FK1); + PhTx: wild type, n = 10 (FK2), n = 14 (FK1); inckk3, n = 10 (FK2), n = 22 (FK1)). e Representative NMJ images immunostained with anti-FK2, -HRP, and -DLG in inc mutants rescued presynaptically or postsynaptically at baseline and after PhTx application. While the FK2 signal fails to increase after PhTx in the presynaptic inc rescue condition, the FK2 signal increase is restored in the postsynaptic rescue. f Quantification of mean FK2 intensity in the indicated genotypes normalized to wild-type values (–PhTx: presynaptic rescue, n = 10; postsynaptic rescue, n = 12; + PhTx: presynaptic rescue, n = 10; postsynaptic rescue, n = 11). Asterisks indicate statistical significance using a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test: (**) p < 0.01; (ns) not significant. Error bars indicate ± SEM. n values indicate biologically independent cells. Additional statistical information and absolute values for normalized data can be found in Supplementary Table 2. Source data are provided as a Source Data file