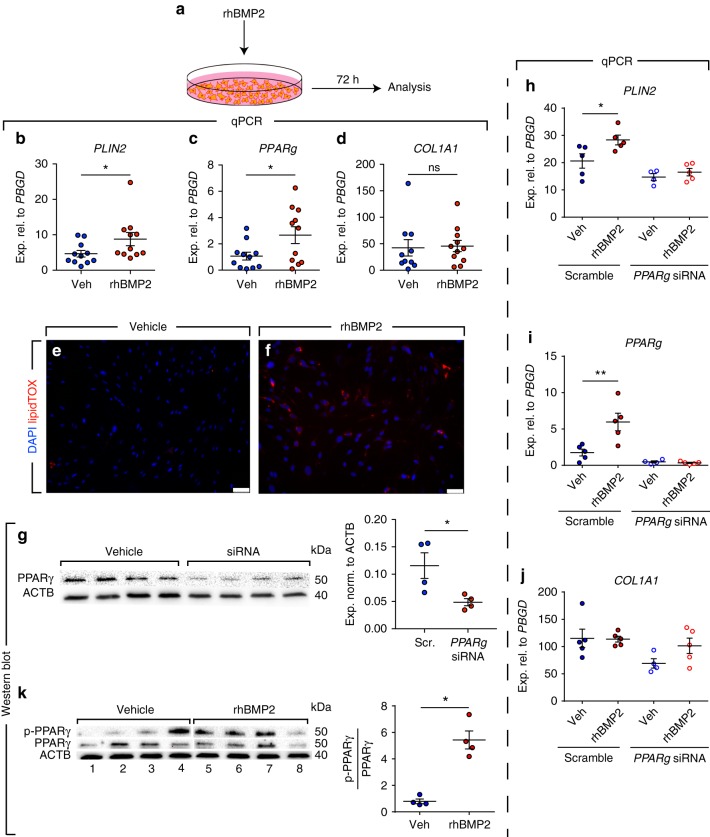
Fig. 6.
rhBMP2 induces PPARγ phosphorylation and lipogenic differentiation in human IPF lung fibroblasts. a Schematic representation of the experimental setup. b–d qPCR analysis of PLIN2, PPARg and COL1A1 in IPF fibroblasts treated with rhBMP2 or vehicle. e, f Staining of rhBMP2- and vehicle-treated cells with LipidTOX (red) and DAPI (blue). g Western blot validating the knockdown of PPARγ protein levels 72 h after siRNA treatment. Quantification of the immunoblot is shown in the right panel. h–j qPCR analysis of PLIN2, PPARg, and COL1A1 in IPF fibroblasts transfected with siRNA against PPARg (for 72 h) and then treated with vehicle or rhBMP2 for 72 h. k Western blot showing the induction of PPARγ phosphorylation in response to rhBMP2 treatment. Lanes 1–4 and lanes 5–8 were run in parallel on different gels under the same conditions. Quantification of the immunoblot is shown in the right panel. Scale bars: e–f 50 µm. Each data point corresponds to one patient and error bars indicate s.e.m. b–d n = 11 per group except for COL1A1 vehicle-treated group (n = 10). g, k n = 4 per group. h–j Scramble/vehicle-, scramble/rhBMP2- and siRNA/rhBMP2-treated groups: n = 5 per group, siRNA/vehicle-treated group: n = 4. Mann–Whitney test was used in (b, d, g, k) and Student’s t-test was used in (c). Kruskal–Wallis test was used in (h–j). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. ns: not significant