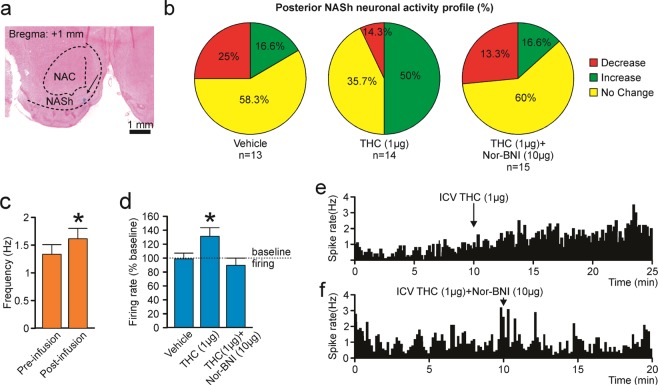
Figure 5.
Effects of ICV THC and nor-BNI on MSN activity patterns in the pNASh. (a) Representative microphotograph showing typical intra-pNASh in vivo MSN recording location. (b) Summary of experimental neuronal groups showing relative changes (no change, increase, or decrease) in firing frequencies following ICV pharmacological treatments. (c) ICV THC significantly increased spontaneous pNASh MSN neuronal firing frequency. (d) ICV THC alone (1 µg/μl) caused a significant increase in spontaneous aNASh MSN neuronal firing frequency rates vs baseline activity. This excitatory effect was reversed by co-administration of the behaviorally effective dose of nor-BNI (10 µg/μl). (e) Sample rastergram showing typical pNASh MSN response pattern following ICV THC (1 µg/µl) infusion (arrows indicate intra-NAc infusion event). (f) Sample rastergram showing typical aNASh MSN response pattern following ICV THC (1 µg/µl) and nor-BNI (10 µg/µl) infusion (arrows indicate intra-NAc infusion event).